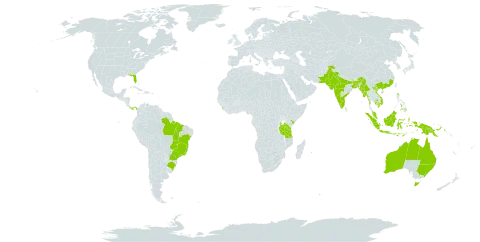
Spreading tree to 28 m high, bole up to 12 m and 50 cm d.b.h. Branchlets angular, glabrous. Phyllodes curved or falcate, acute or subacute, 10-16 by (1.2—)1.5 —2(—3) cm, 4-8(-10) times as long as wide, glabrous, greyish green, major veins and margins not yellow, pulvinus 4-6 mm, with at the top a gland, swollen, c. 1 mm in diameter, with a narrow orifice; major prominent longitudinal veins 3 or 4, at the base running together towards the basiscopic margin or in the middle and with several crowded, somewhat anastomosing secondary veins. Spikes somewhat interrupted, 8(-10) by 0.6-0.7 cm, on glabrous peduncles, 0.5-0.8 cm, paired in the axils of the distal phyllodes. Flowers golden yellow, fragrant, pentamerous. Calyx 0.7-1 mm, glabrous; lobes triangular, 0.2 mm. Corolla 1.7-2 mm, glabrous; lobes reflexed, oblong, c. 1 mm. Stamens c. 3 mm. Ovary densely puberulous. Pod brown, often glaucous, flat, contorted, with undulate margins, c. 6.5 by l-1.5(-2.5) cm; valves sub-woody, glabrous, veins transverse, anastomosing. Seeds black, transverse, elliptic, c. 5 by 3.5 mm; areole large and almost closed; funicle orange, 3.8-5 by 3-5.5 mm, completely encircling the seed.
An evergreen tree. It grows to 17-20 m height and spreads about 5 m wide. It has lots of leaves and forms a dense round crown. The stems are erect and stout. The bark is greyish-green. It is rough and hard. The branches are angular. The leaves (phyllodes) are sickle shaped. They taper to a blunt tip and are 10-20 cm long. They are 1.5 to 3.5 cm across. The 3 main veins are prominent. The leaves are shiny and dark green. The flowers are dull golden rods. They are about 8 cm long. These rods occur in pairs in the angles of the leaves. The pods are woody, twisted and hard. These ear like pods are distinctive. They are about 5-7 cm long and 1.5 cm wide. They are dark brown when ripe. They contain black seeds arranged diagonally. The seeds are attached by a bright red aril.
Trees, evergreen, to 20 m tall. Bark gray-white, smooth. Branches pendulous; branchlets angular, glabrous, with conspicuous lenticels. Phyllodes falcate-oblong, 10-20 × 1.5-4(-6) cm, conspicuous main veins 3 or 4, both ends attenuate. Spikes 1 to several, fasciculate, axillary or terminal, 3.5-8 cm. Flowers orange-yellow. Calyx 0.5-1 mm, shallowly dentate. Petals oblong, 1.5-2 mm. Filaments 2.5-4 mm. Ovary densely puberulent. Legume contorted when mature, 5-8 × 0.8-1.2 cm, valves woody. Seeds ca. 12, black, ca. 5 × 3.5 mm. 2n = 26*.