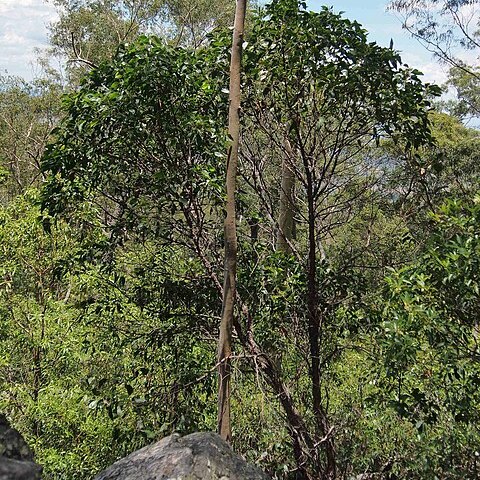
Tree 4–20 m high. Bark rough, furrowed and somewhat shaggy. Branchlets stellate-hairy; hairs golden on new shoots. Phyllodes inequilaterally narrowly elliptic to lanceolate, ± falcate, 9–30 cm long, 2–6 cm wide, acuminate (except young plants), ± glabrous, with 3 prominent main veins (only the lowermost reaching apex) and obviously reticulate in between; basal gland elongated, with 3 or 4 additional smaller glands in indentations or occasionally on short projections along upper margin. Inflorescences in axillary racemes or terminal panicles, sometimes leafy; raceme axes 2–10 cm long, golden stellate-puberulous; peduncles 6–28 mm long, 1 to several per node, yellowish stellate-puberulous; heads globular, 4.5–6 mm diam., 30–60-flowered, cream-coloured. Flowers 5-merous; sepals ⅔–¾-united. Pods flat, to 12 cm long, 1.5–2.5 cm wide, thinly coriaceous, transversely reticulate, glabrous. Seeds transverse, elliptic, 6–7 mm long, dull, black, arillate.