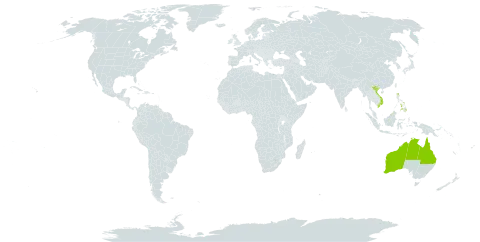
Shrub or tree 3–8 m high. Branchlets acutely angled but normally ± terete by 20–30 cm below apex, usually sericeous, sometimes glabrous. Young shoots silvery sericeous, sometimes glabrous. Phyllodes obliquely narrowly elliptic, 10–20 cm long, normally 2–5 cm wide, with unequal base, usually sericeous; mucro 1–3 mm long; normally 3 prominent veins per face confluent and contiguous with abaxial margin at base; minor veins forming a somewhat open longitudinally orientated reticulum; glands basal and at base of mucro on at least some phyllodes. Inflorescences rudimentary racemes with axes to 0.5 mm long; peduncles 3–7 mm long, sericeous, sometimes glabrous; spikes normally 2–4 cm long, golden; bracteoles linear-spathulate, 1–1.5 mm long. Flowers 5-merous; sepals united. Pods tightly and often somewhat irregularly coiled, 2.5–4 mm wide, thinly crustaceous to coriaceous-crustaceous, ± glabrous, remaining as entangled clumps following dehiscence. Seeds longitudinal, oblong-elliptic, 3.5 mm long, shiny, dark brown; aril bright yellow.
A straggling spreading shrub. It keeps its leaves throughout the year. It can grow up to 2-8 m tall. It can spread to 4 m across. The branches are angular and hairy. The bark is smooth and grey. The leaves (phyllodes) are grey green and silvery white. They are carried one after the other along the stem. In wetter locations the leaves are larger and darker green. They are 10-18 (-25) cm long and 1-2 (-9) cm wide. They have 2 or 3 clearly seen veins. These veins run along the leaf and join towards the base. The tip of the leaf has a thick sharp point. The flowers are yellow spikes 3-6 cm long. The flowers are slightly scented. The pods are produced in tight clusters. They are twisted and curled when mature. They are 3-5 cm long by 0.2-0.5 cm wide. The seeds are small and black. Where the seed is attached to the pod it is yellow or red.