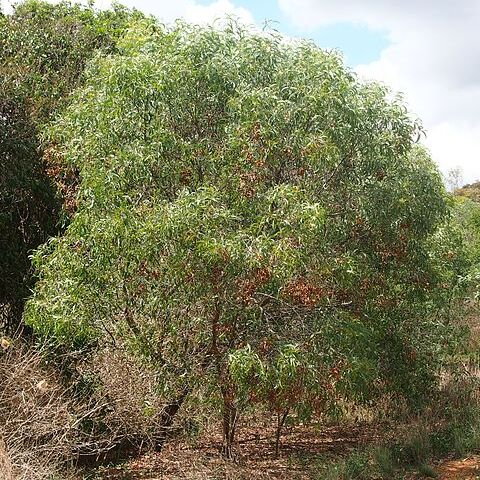
Tree to 15 m high, rarely a shrub to 4 m. Bark 'ironbark' type, dark grey to almost black. Branchlets angular towards apices, lenticellate, glabrous. Phyllodes narrowly elliptic, attentuated towards both ends, markedly falcate, (8–) 11–20 (–27) cm long, (6–) 10–35 (–55) mm wide, thinly coriaceous, glabrous, with 3 prominent main veins (the lower 2 often confluent towards base and the uppermost sometimes confluent with upper margin before reaching apex); minor veins 1–3 per mm, longitudinal, occasionally anastomosing; gland usually 1, basal, conspicuous. Spikes 3.5–9.5 cm long, yellow to golden. Flowers 5-merous; calyx 0.4–0.9 mm long, sinuate or dissected to ¼ of length, with fimbriate margins, ± glabrous; corolla 1.3–2 mm long, dissected to ½ of length, glabrous; ovary densely pubescent. Pods slightly or variably constricted between and raised over seeds, curved, curled or twisted, 8–15 cm long, 2–3.5 (–5) mm wide, thinly coriaceous to chartaceous, glabrous. Seeds longitudinal, oblong-elliptic, 3–4 mm long, dark brown; pleurogram U-shaped; funicle-aril massive, longer than seed, yellow-orange.
An evergreen tree. It grows to 7-12 m high with 2-5 m spread. The stem is erect and branching. It is a graceful tree. It has a rounded crown. The bark is rough and dark. It is lightly cracked or chequered near the base. The inner bark is red. The young branches are angular. The leaves (phyllodes) are narrow and curved. They are 13-23 cm long and with 3 prominent veins. Leaves are 1.5 to 3 cm wide and shiny. The flowers are yellow rods 4-7 cm long. They occur in pairs on stalks in the angles of leaves. The pods are narrow (0.1-0.3 cm) and 10-13 cm long. They are papery. They coil and twine into clusters. They are dark brown when ripe. They contain several black seeds. The seeds are 4 mm by 2.5 mm.