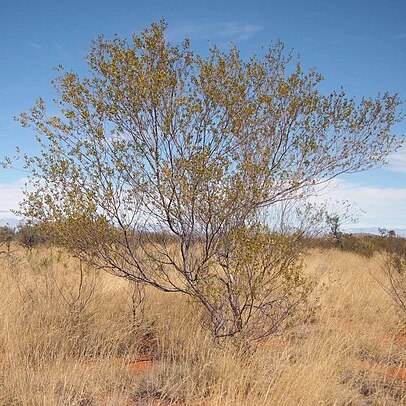
Openly branched, erect, normally rather straggly shrub 1–4 m high, becoming rather bushy in well-watered sites. Branchlets red to brown, lenticellular, glabrous, resinous-viscid, scarred where phyllodes have fallen. Stipules 0.5–1.5 mm long, erect, often enveloped in resin. Phyllodes patent to inclined, variable, ±asymmetrically narrowly elliptic to oblong-elliptic or oblong-obovate, (6–) 7–25 (–30) mm long, (1.5–) 2–4 (–5) mm wide with l: w ratio = 3–10, pungent with a slender cusp, rigid, green, glabrous; midrib prominent, rarely with an obscure second vein, lateral veins obscure or absent; pulvinus 0.5 mm long, yellow. Inflorescences simple, 1 per axil; peduncles 1–2 (–2.5) cm long (often exceeding the phyllodes), glabrous; heads globular, c. 9 mm diam. (fresh), densely 50–90-flowered, golden. Flowers mostly 5-merous; sepals free, linear-spathulate. Pods rounded over and slightly constricted between seeds, 2–7.5 cm long, (3–) 4–5 (–10) mm wide, firmly chartaceous, glabrous, somewhat viscid when young. Seeds longitudinal, elliptic to ovate, 3.5–4.5 mm long, dark brown, slightly mottled, cream on periphery and bordering pleurogram, exarillate.
More
A small shrub. It can be 2-3 m high and 1-3 m across. The small branches are slender and round in cross section. They are sticky. Resin which comes from the smooth hairless stems has a sweet smell. The leaves (phyllodes) are 1-2 cm long and 0.2-0.5 cm across. They are rigid and pointed. This makes them spiky. They have a central vein. The flower heads are bright yellow balls. Either one or two flower heads occur in the angles where leaves join. The pods are 2-4 cm long by 0.2-0.4 cm wide. They are flat and thin. The seed are rounded, small and soft.
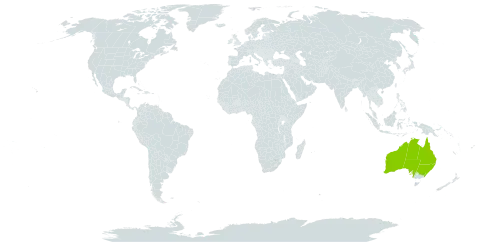
Widespread in the arid zone, growing in red sand on plains or dunes, or sometimes on rocky slopes, often in mulga scrub, spinifex country or eucalypt open woodland.
More
It is a tropical plant. It occurs in inland Australia. It grows in sandy soils. It needs a sunny position. It can tolerate fire. It can grow in arid places.
Grows in red sand on plains or dunes, or sometimes on rocky slopes, often in mulga scrub, spinifex country or eucalypt open woodland.