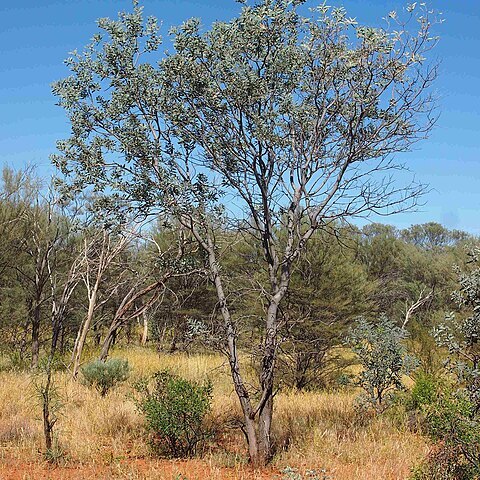
Shrub or tree 3–12 m high. Branchlets often pruinose, glabrous. Phyllodes normally spreading widely, linear to linear-elliptic, straight or curved, 7–17 cm long, 6–20 (–30) mm wide, obtuse to subacute, thick, coriaceous, subglaucous to glaucous, glabrous; midrib and marginal veins prominent; lateral veins obscure; glands 2–5, lowermost largest and basal. Inflorescences 6–20-headed racemes; raceme axes 3-15 cm long, stout, often pruinose, glabrous; peduncles 1–4 cm long, mostly 2 or 3 together along raceme axes, rather stout, glabrous; heads globular, 7–8 mm diam., densely 55–110-flowered, light golden. Flowers 5-merous; sepals united; bracteole laminae and sepal apices densely golden-hairy. Pods narrowly oblong, to 12 cm long, 9–17 mm wide, chartaceous to thinly coriaceous, often pruinose, glabrous. Seeds transverse to oblique, ovate to oblong-elliptic or suborbicular, 5–6 mm long, dull, black; funicle flat, liguliform; aril small.
More
A small tree 3-10 m high and spreading 3-5 m across. It normally has several stems. The bark is dark and fibrous. The leaves (phyllodes) are 6-15 cm long by 0.5-3 cm wide. They are flat and stiff. They are curved, leathery and with a bluish bloom. They have one prominent vein and a large gland at the base of the leaf. The edge of the leaf is prominent. The flower heads are balls. They occur singly or in pairs. They are bright yellow. The pods are 3-10 cm long by 1-1.5 cm across. They are flat, leathery and with a bluish bloom. They are waxy. They are raised over the seeds. The seeds are nearly round and 5 mm across. They are black to dark brown when ripe.