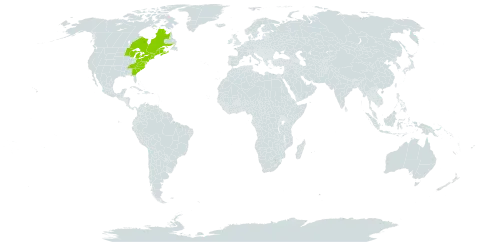
A tree that loses its leaves. It grows 6 m tall and spreads 3 m wide. The stem is erect and slender. The bark has stripes. The leaves have 3 lobes and are large. They grow opposite each other. The leaves turn yellow in autumn. The seeds are winged.
| Life form | perennial | ||||||||||||
| Growth form | tree | ||||||||||||
| Growth support | free-standing | ||||||||||||
| Foliage retention | deciduous | ||||||||||||
| Sexuality | hermaphrodite | ||||||||||||
| Pollination | entomogamy | ||||||||||||
| Spread | - | ||||||||||||
| Mature width (meter) | 2.75 | ||||||||||||
| Mature height (meter) | 5.25 - 8.15 | ||||||||||||
| Root system | - | ||||||||||||
| Rooting depth (meter) | 0.7 | ||||||||||||
| Root diameter (meter) | - | ||||||||||||
| Flower color | |||||||||||||
| Blooming months |
|
||||||||||||
| Fruit color | |||||||||||||
| Fruiting months |
|
||||||||||||
| Nitrogen fixer | - | ||||||||||||
| Photosynthetic pathway | c3 |
| Light |
|
| Soil humidity | |
| Soil texture | |
| Soil acidity | |
| Soil nutriment | - |
| Hardiness (USDA) |
| Uses | beverage environmental use fuel material medicinal wood |
| Edible | saps |
| Therapeutic use | Emetic (bark), Laxative (bark), Orthopedic Aid (bark), Cold Remedy (bark), Cough Medicine (bark), Misc. Disease Remedy (bark), Dermatological Aid (bark), Respiratory Aid (unspecified), Unspecified (unspecified), Veterinary Aid (unspecified), Antihemorrhagic (unspecified), Kidney Aid (unspecified), Orthopedic Aid (unspecified), Venereal Aid (unspecified), Tonic (unspecified), Cancer (unspecified), Eruption (unspecified) |
| Human toxicity | - |
| Animal toxicity | - |
| Mode | cuttings graftings seedlings |
| Germination duration (days) | 30 - 365 |
| Germination temperacture (C°) | 11 - 12 |
| Germination luminosity | - |
| Germination treatment | soaking |
| Minimum temperature (C°) | -23 |
| Optimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Size | - |
| Vigor | - |
| Productivity | - |

| LSID | urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:781446-1 |
| WFO ID | wfo-0000514839 |
| COL ID | 94GR |
| BDTFX ID | - |
| INPN ID | - |
| Wikipedia (EN) | Link |
| Wikipedia (FR) | Link |