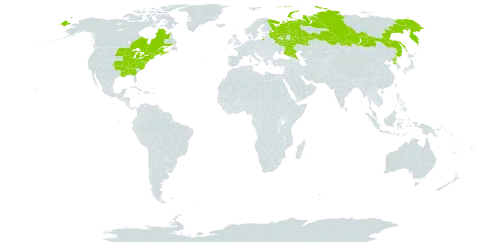
Climax tree to 40 m; bark medium-gray, becoming roughened with loose-edged plates; lvs flat, about as wide as long, usually glabrous beneath except for a few tufts of hairs in the vein-axils, (3)5-lobed with rounded sinuses, the lobes usually bearing a few large sharp teeth, the central lobe usually with nearly parallel sides to a pair of large teeth at about mid-length; fls in umbels from the terminal or uppermost lateral buds, appearing as the lf-buds open, drooping on slender, hairy pedicels to 8 cm; cal gamosepalous, 2.5–6 mm, ± hirsute; pet none; disk extrastaminal; ovary and fr glabrous; mericarps of the fr 2.5–4 cm, the seed-bearing basal parts diverging at right angles to the pedicel, the wings curved forward, divergent at an angle of 120° or less; 2n=26. Rich to fairly dry woods, especially in calcareous soils; N.S. and N.B. to Minn. and e. S.D., s. to N.J., Del., w. Va., n. Ga., Tenn., and Mo. (Saccharodendron s.; Acer saccharophorum) Plants intermediate toward A. barbatum, occurring along the s. boundary of our range, have been called var. schneckii Rehder, or var. regelii (Pax) Rehder, the latter name however based on a specimen of A. barbatum. Spp. 2–4 often treated as parts of a single sp.
More
A deciduous broad leafed tree. It grows 40 m high and spreads 10 m across. The stem is stout. It has grey bark. There are lines running up the bark on the trunk. Branches from low down. The leaves are dark green on top and silvery on the under side. The leaves are divided like the fingers on a hand. There are 5 leaf lobes with teeth like edges to the leaf. The leaves are 8-18 cm long. The leaves turn bright orange, red or yellow in the autumn. The flowers are greenish-yellow. They occur in branched stalks with a flat top. These stick upwards. The seeds occur in central containers with wings at a slight angle. There are many cultivated varieties.
It is a temperate plant. A plant native to north America. It requires light fertile soils. It needs a protected position and can stand shade when young but full sun when mature. It is frost resistant but drought tender. It cannot tolerate coastal locations. It cannot tolerate pollution. It suits hardiness zones 4-8. Arboretum Tasmania.
More
Found in a variety of soil types, doing best in deep rich well-drained soils from sea level to 1,600 metres. Rich usually hilly woods.