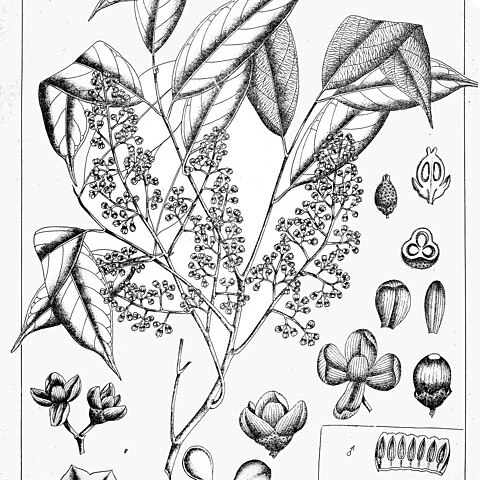
Trees or shrubs, 2-20 m tall. Branches grayish, pale to yellowish lepidote, sometimes glabrescent. Leaves alternate, to 50 cm; petiole and rachis lepidote or glabrous; petiolules 1-15 mm, sometimes slightly inflated, sparsely to densely lepidote, sometimes glabrescent; leaflets 3-9, alternate to subopposite; leaflet blades elliptic, oblong, ovate-lanceolate, or lanceolate, 5-20(-30) × 2-7.5(-11.5) cm, papery to leathery, both surfaces glabrous or adaxially lepidote only on midvein and abaxially lepidote on veins only or on entire surface, midvein abaxially prominent and adaxially depressed, secondary veins (8-)12-15(-16) on each side of midvein, abaxially prominent or depressed, and adaxially flat, prominent, or depressed, base rounded or ± oblique by being cuneate and conspicuously decurrent on one side and rounded on other, apex acuminate to obtuse. Thyrses axillary, botryose, usually shorter than leaves, 2-15 cm in male plants but shorter and with fewer flowers in female plants, densely lepidote or stellately lepidote, few flowered or sometimes with just 1 flower. Flowers unisexual, 3-5 mm in diam. Pedicel 2-3 mm, as long or slightly longer than flower buds, nodiferous, lepidote. Calyx cup-shaped, 1-2 mm, densely lepidote, 3-5-lobed, lobes rounded or sometimes nearly truncate. Petals 3 or 4, suborbicular, ovate, obovate, or oblong, 2-6 mm, concave, outside sometimes sparsely lepidote near base, otherwise glabrous, free from staminal tube. Staminal tube turbinate to campanulate, 2-5 mm, both surfaces gla-brous or outside sparsely lepidote, apical margin entire or crenate/serrulate; anthers (5 or)6(-12), linear, oblong, or ovoid, ca. 0.5 mm, inserted just above inside middle of tube, included or very slightly exserted, both ends acute. Ovary shortly conical, stellately lepidote, 2-or 3-locular, with 2 ovules per locule; style absent; stigma conical, glabrous, 3-lobed. Infructescences 6-10 cm, lepidote. Fruit dehiscent, ellipsoid, globose, or pyriform with base gradually constricted into a 3-16 mm stipe, 1-3 cm in diam., 3-locular, rugose, lepidote, apex rounded, concave, or acute; pericarp woody, hard when dry; calyx persistent, spreading and ± reflexed, lepidote, margin 3(or 4)-dentate. Seeds 1-3 per fruit, completely surrounded by a fleshy usually red aril. Fl. May-Dec, fr. almost year-round.
A small tree. It grows to 10-15 m tall. It can be 30 m high. The leaves are alternate and compound. The flowers are about 1 mm across and yellow. They are in large groups. The fruit is about 12 mm across. They are white to pink. They are fleshy and the seeds have a fleshy layer around them. This is white to red.