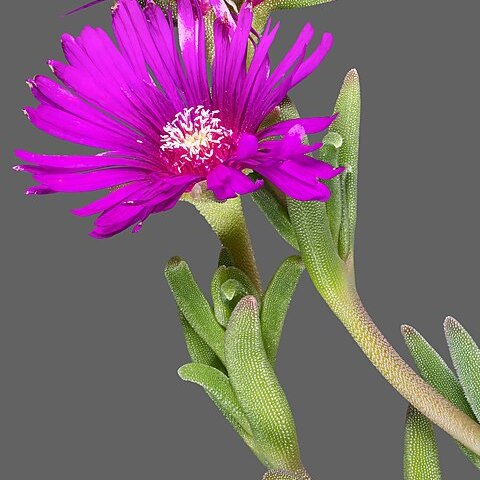
Succulent or subsucculent annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs, less often shrubs. Leaves simple, alternate, opposite or verticillate, sometimes crowded, often with an expanded membranous base, exstipulate or with membranous stipules. Inflorescences cymose, loosely dichasial to umbelliform or glomerulate (flowers sometimes solitary), axillary or terminal. Flowers regular, hermaphrodite, rarely unisexual. Calyx of 5, less often 4 or 3, members, polysepalous or gamosepalous, usually herbaceous and persistent. Petals absent. Staminodes sometimes present, then often petaloid. Stamens 5-many, hypogynous or episepalous, sometimes fascicled, when definite alternate with the calyx-lobes. Ovary superior or inferior, of 2–5-many united (rarely free) carpels, or of 1 carpel; loculi as many as carpels; ovules one, few, or many per loculus; placentation basal, axile, apical or parietal but not free-central. Fruits usually capsular, loculicidal or circumscissile, sometimes indehiscent, rarely mericarpic. Seeds usually subreniform, rarely strophiolate; embryo usually curved
Herbs, annual or perennial, subshrubs, or shrubs, succulent. Stems erect or prostrate. Leaves simple, rarely pinnate, mostly opposite, sometimes alternate, in many species fleshy, margin entire, rarely with teeth; true stipules absent, sometimes a stipule-like sheath present at base of petiole. Inflorescences terminal or seemingly axillary cymes, or solitary flowers. Flowers bisexual, rarely unisexual, actinomorphic, perigynous or epigynous. Nectaries separate or in a ring around ovary. Tepals (4 or)5(–8), connate below into a tube. Petals absent or present. Stamens 3 to many, free or connate at base, outermost often as filamentous staminodes; anthers dehiscing by longitudinal slits. Ovary inferior, syncarpous; carpels 2 to many; ovules 1 to many, on long funicles, mostly campylotropous; placentation axile or parietal, sometimes basal-parietal. Stigmas as many as carpels. Fruit a hygroscopic or circumscissile capsule, more rarely a berry or nut. Seeds with slender embryo curved around perisperm, rarely with an aril; endosperm scanty or absent.
Herbs or shrubs, glabrous, papillose, hairy or scaly. Leaves alternate or opposite, simple, flat, terete or triquetrous, often with expanded membranous base, usually succulent. Flowers terminal or axillary, sessile or pedicellate, solitary, clustered or in thyrses; bracts present or absent; flowers actinomorphic, bisexual. Perianth segments 4 or 5, equal or unequal, persistent, often coloured inside. Petals 0. Stamens 4 to many, alternate with perianth segments or evenly distributed; staminodes 0 to many, often petal-like. Ovary superior, half-inferior or inferior; styles as many as locules; locules 1 to many; ovules 1 to many per locule; placentation axile and apical or basal, or parietal. Fruit a capsule opening loculicidally or septicidally, or circumsciss (and then with a cap or operculum), or indehiscent, smooth or variously winged or ridged; placenta often enlarged in fruit to form a tubercle. Seeds 1 to many, often pea-shaped or comma-shaped, usually patterned or papillose.
Ovary superior, of 1–5 united carpels; loculi as many as carpels; ovules 1–? per loculus; placentation parietal, axile or apical
Leaves simple, opposite, alternate or sometimes crowded, exstipulate, sometimes with small stipuliform lobes at base
Stamens 5–?, hypogynous, sometimes in pairs or in fascicles, when definite alternate with the perianth segments
Perianth segments 5, united below into a tube or almost free, ± herbaceous, imbricate or valvate, persistent
Annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs, mostly succulent or subsucculent, glabrous or pubescent
Seeds usually subreniform, not strophiolate; embryo usually curved
Inflorescences solitary or in groups, axillary
Fruit capsular, loculicidal or circumscissile
Flower hermaphrodite, regular