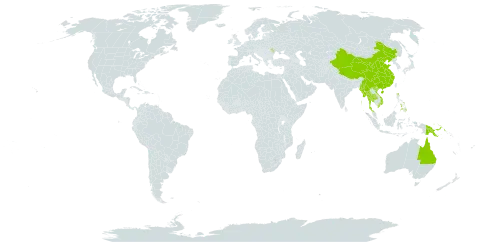
Shrub to 3 (–5) m high. Stipules linear, 2–4 mm long. Leaves petiolate; petiole 3–28 mm long; lamina cuneate-oblanceolate, spathulate, rarely elliptic, 35–270 mm long, 15–90 mm wide; margin crenate with 8–12 antrorse, spineless teeth per side; teeth 1–2 mm long. Inflorescence terminal, up to 170 mm long. Male flowers 2–4 per glomerule; pedicels up to 2 mm long; sepals 2 or 3, splitting equally, ovate, c. 1 mm long, c. 1 mm wide; stamens 4. Female flowers: pedicels c. 1 mm long; styles erect to recurved, 3–5 mm long, entire. Fruit subglobose, 5–6 mm long, c. 10 mm diam. Seeds 3.5–5.5 mm long, 2.7–5 mm wide, yellow-brown.