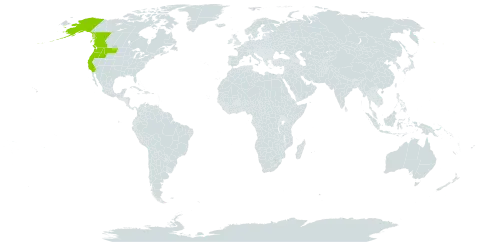
A deciduous tree. It grows 12-15 m high. It usually branches into several trunks. The lower branches hang downwards. The bark is thin and pale grey. The leaves are large and have coarse teeth around the edge. They are dark green above and paler grey-green underneath. There is often fine orange hairs underneath. The male flowers are catkins borne at the tips of the branches. They are yellow. The fruit are woody and cone like. They are 2.5 cm long.