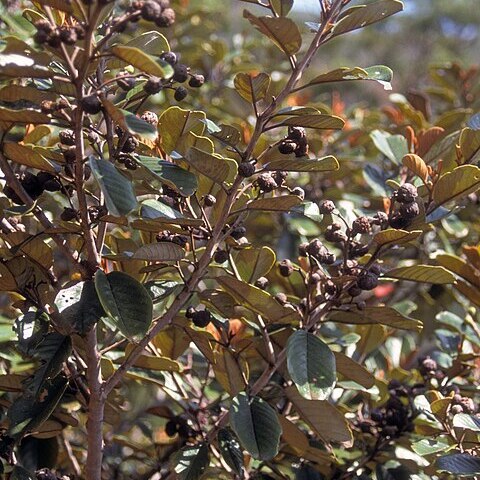
Trees or rarely shrubs, evergreen. Spines absent. Branches (in most species) horizontal, in layers (‘pagoda-type’ branching). Indumentum of simple, unbranched trichomes, straight, flexuose, tortuous or crisped. Glands absent. Leaves alternate, simple, petiolate, distichous on smaller branches (except sometimes A. whitei), penniveined, intramarginal veins absent, margin entire, straight or undulate; translucent dots absent; upper surface green, glabrous or glabrescent; lower surface with dense short tomentum, often white; domatia absent; stipules 2 per leaf, free from each other, entire, caducous. Inflorescences dichasially or trichasially cymose, arranged into axillary racemes; flowers bisexual, protandrous, 5-merous; calyx 5-lobed, spreading, adaxially keeled; petals 5, cymbiform, caducous; stamens 5, each enclosed within a petal; anthers broadly sagittate with an appendage, versatile, basifixed, dehiscent by longitudinal slits; nectary disc thick, fleshy, filling the floral tube; style solitary, 2–3 (–4)-fid, rudimentary before anthesis, elongating after anthesis; ovary partly inferior, 2–3 (–4)-locular. Fruits drupaceous, tardily dehiscent, the lower portion united with the calyx tube; epicarp thin, black, shiny, with ring-scar marking position of fallen sepals; mesocarp (when present) spongy to powdery, reddish; endocarpids hard, woody, often apiculate, dehiscing along the ventral suture and partly down the dorsal suture, each enclosing a single seed. Seeds often persistent on torus after remainder of fruit has fallen away, grey, with glossy hard testa, enclosed by membranous reddish brown aril.
More
Trees or shrubs, evergreen. Buds and young branches often ± densely brownish pubescent. Leaves alternate, with small, caducous stipules; leaf blade ovate to obovate or elliptic to lanceolate, rarely nearly cordate, papery to leathery, pinnately veined, abaxially usually glabrous, adaxially whitish to rusty pubescent, margin entire. Flowers bisexual, 5-merous, many in di-or trichotomous, axillary or rarely terminal cymes. Calyx tube patelliform to hemispherical; sepals 5, triangular, adaxially keeled. Petals 5, clawed, cucullate. Stamens 5, enfolded by petals. Disk mainly thick, nectariferous. Ovary inferior, immersed in disk, 2-or 3-loculed, with 1 ovule per locule; style short, often divided into 2 to 3 slightly capitate stylar branches, basally often densely whitish to yellowish pubescent or glabrous. Fruits drupaceous, globose or broadly ovoid, at base surrounded by persistent calyx tube; mesocarp thick, initially fleshy, later dry and mealy; endocarp splitting longitudinally into 2 or 3, hard, leathery, 1-seeded endocarpids. Seeds ± completely enclosed by a membranous, reddish to brownish aril; testa smooth, crustaceous; embryo straight; endocarp cartilaginous.