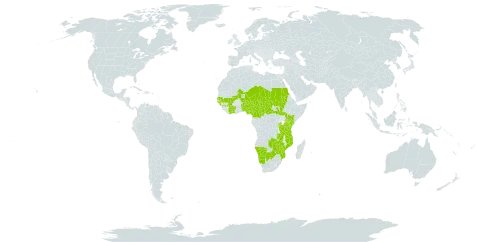
A large climbing herb. It grows 2-8 m high. It has soft stems. These arise from a large fairly soft underground rootstock. The young branches are densely hairy. It has tendrils. The leaves are simple. The leaf blade is 20 cm across. It is broadly oval. There are teeth along the edge. The base is heart shaped. The flowers are in clusters. They are small and greenish-yellow. The fruit is 1 cm across. The fruit are blackish berries. The fruit have large seeds. The seeds are shiny and brown. They are 7 mm long by 4 mm wide.
Leaves simple; petiole up to 13 cm. long, pubescent or glabrous; leaf-lamina up to 20 cm. in diam., from very broadly ovate to circular, entire or shallowly 3–5-lobed, or more rarely deeply lobed, apices of lobes rounded or acute, margins serrate or crenate, base cordate with a rounded sinus c. 2 cm. deep, pubescent above when young or glabrous, varying from tomentellous (when young) to pubescent or glabrous below.
Inflorescence of moderately dense or rather lax cymes; penduncle up to c. 6 cm. long, from subtomentose to glabrescent; tendril arising from the base of the inflorescence-rhachis or below; pedicels less than 1 mm. long.
Climber or liane, or sometimes prostrate; branches densely pubescent when young or entirely glabrous, striate.
Calyx c. 1·5 mm. in diam., ± salver-shaped or cyathiform, glabrous, margin entire or shallowly lobed.
Disk reddish, c. 1/2 the length of the ovary, cupular.
Petals reddish, up to 1·5 mm. long, oblong, glabrous.
Seeds shining brown, c. 7 × 4 mm., ellipsoid.
Stamens c. 1/2 the length of the petals.
Fruit subglobose, c. 1 cm. in diam.
Flowers in subcapitate clusters.