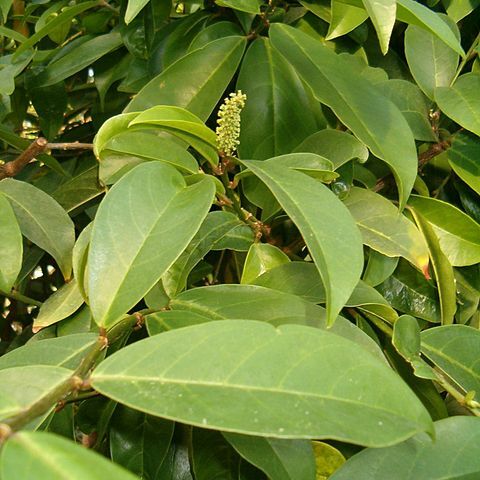
Trees, rarely shrubs, up to 30 m tall; young twigs glabrous to very shortly pubescent. Stipules linear, 4-6 × 1.5-2 mm, caducous; petiole 3-10(-17) mm, glabrous to pubescent; leaf blade oblong, elliptic, or obovate, (5-)10-23(-32) × (2-)3-10 cm, leathery or thickly papery, glabrous except sometimes midvein pilose, or abaxially reddish pubescent, shiny, usually drying dark green (sometimes grayish or reddish) adaxially, slightly lighter abaxially, base acute to rounded, apex acute to rounded, sometimes slightly emarginate or acuminate, usually mucronate; domatia absent; midvein flat to impressed adaxially, lateral veins (5-)7-11 pairs, tertiary veins reticulate. Inflorescences axillary or terminal, axes glabrous to pubescent, robust, males 6-17(-25) cm, 3-8(-14)-branched, females and fruiting (4-)10-18 cm, unbranched or more rarely up to 4-branched. Male flowers sessile; calyx 1-1.5 mm, cup-shaped, 3-or 4(or 5)-lobed, divided for 1/4-1/3, glabrous to pubescent outside, reddish long pubescent at base inside, margin fimbriate, apex of lobes obtuse to rounded; disk annular, consisting of free lobes or enclosing stamens and pistillode, glabrous; stamens 3 or 4(or 5), 2-3 mm; rudimentary ovary clavate to cylindric. Female flowers: pedicels 0.5-1(-2) mm, 2-4(-9) mm in fruit; calyx 3-lobed, otherwise as in male; disk glabrous; ovary glabrous or pilose; stigmas 3 or 4(-6). Drupes ellipsoid, laterally compressed, 5-11(-?18) × 4-7 mm, glabrous or pilose, red to black when ripe; style (sub)terminal. Fl. Mar-May, fr. Jun-Nov. x = 13.
More
Shrub or small tree to 4 (–10) m high, evergreen. Stipules not seen. Leaves: petiole 1–13 mm long; lamina elliptic to cuneate-obovate, 20–220 long, 10–90 mm wide, base cuneate, margin entire or weakly to strongly sinuate, tip acute, acuminate to obtuse, mucronate. Male flowers c. 2 mm long; calyx lobes orbicular, c. 0.5 mm long; disc glabrous; stamens 3. Female flowers 4–4.5 mm long; pedicel c. 1.2 mm long; calyx 5-lobed, cupular, c. 1.2 mm long, 2.5 mm diam.; disc annular, glabrous; styles 2, recurved, terminal, 1–1.2 mm long. Fruit globose, purple-black to purple-red, 13–15 mm long, 12–15 mm diam.
A small bushy tree. It is often 3-6 m tall. It can be up to 15-30 metres high. The leaves tend to be long and narrow and shiny. They are dark green. They are pointed at the tip and more rounded at the base. The leaves are 10-15 cm long by 5-7 cm wide. The male and female flowers are separate, on separate trees. Female flowers producing fruit are on the ends of branches. A spike of dark reddish black berries is produced. The berries are about 1 cm across and have one seed inside. They hang in a large cluster. There are 20-50 in a cluster.
A tropical plant. It can probably grow up to 1000 m altitude in the tropics. In Indonesia it grows between 50-1,400 m above sea level. It can stand light frost. They can grow on a variety of soils. They are common and widely distributed in open places and secondary forest throughout the Philippines. It can tolerate salt. It suits the humid tropical lowlands. It suits hardiness zones 10-12. In XTBG Yunnan.
More
Wet evergreen forest, dipterocarp forest and teak forest; on river banks, at forest edges, along roadsides; in bamboo thickets; in semi-cultivated and cultivated areas; in shady or open habitats; usually in secondary but also in primary vegetation.
Grows in notophyll to mesophyll vineforest on a variety of substrates.
The fruit are eaten raw when ripe or cooked. They are acid so are often better as jam, jellies and wine. Because the fruit is high in pectin it makes good jams and jellies. The young leaves are eaten raw or steamed with rice. They are used as a spice or flavouring. CAUTION The bark is poisonous.
It grows from seeds. These can be planted, but trees also grow naturally from seed. Trees can be produced by budding, grafting or from cuttings. Aerial layering can also be used. Spacing should be about 12 to 14 metres between trees. Some male trees need to be present for cross pollination. When female trees produce fruit without male trees, the seed from these fruit normally will not germinate.