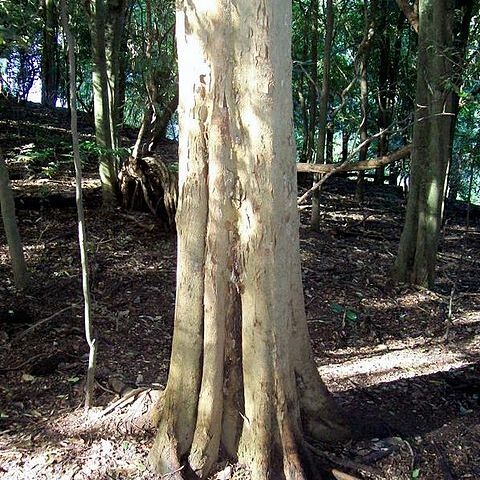
Monoecious, deciduous or semideciduous shrubs or trees, often buttressed. Innovations densely or sparsely, whitish-grey to rufous, appressed-pubescent. Indumentum consisting of bulbous-based, unicellular, finely tuberculate hairs and multicellular, glandular hairs. Older branches glabrous, lenticellate, bearing lateral and terminal buds. Stipules lateral, extrapetiolar, subulate, caducous. Leaves alternate, petioled, glabrous, coriaceous, triplinerved at base or pinnately nerved. Inflorescences ♂, ♀, or very rarely ♂♀, axillary; bracts minute, caducous. ♂ Inflorescences a condensed, multi-flowered raceme, borne on the lower parts of the new shoots; ♂ flowers short-stalked, globular, 4-5-merous; perianth lobes membranous, imbricate in bud, sparsely appressed pubescent outside; stamens glabrous, filaments subulate, inflexed in bud, anthers ovoid-subreniform, non-apiculate, introrse; pistillode absent, replaced by a cluster of whitish to silvery, erect, soft, simple hairs. ♀Flowers solitary in the axil of the upper leaves of the new shoot, or borne in a 2-3-flowered mixed (♂♀) racemose inflorescence; long-stalked; perianth lobes 4-5, long-persistent; staminode absent; ovary sessile, ovoid-ellipsoid, terete to angular; stigmatic arms tubular; ovule anatropous. Drupe fleshy, ovoid-globose, faintly 3-5-angular or ± terete, glabrous; endocarp hard and persistent. Seed exalbuminous, coat membranous, few cells thick; embryo curved, hypocotyle ascending, cotyledons more or less equal, involute. Mode of germination unknown.
More
Trees or shrubs, deciduous or semideciduous, monoecious. Leaves alternate, pinnately veined (in Australia); stipules extrapetiolar, free. Inflorescence axillary, unisexual, rarely with male and female flowers; bracts minute, caducous. Male inflorescence a condensed, many-flowered raceme, in lower axils of new shoots. Male flowers: pedicels short; perianth lobes 4 or 5, membranous, imbricate in bud; stamens 4 or 5, inflexed in bud, included or exserted at anthesis; anthers introrse; pistillode absent. Female inflorescence in upper axils of new shoots, 1-flowered, sometimes 2 or 3 flowers of both male and female. Female flowers: pedicels long; perianth lobes 4 or 5, imbricate in bud; staminodes absent; ovary sessile; stigmas tubular. Fruit a drupe, slightly 3–5-angular or terete. Seed with curved embryo; endosperm absent.
Trees or shrubs, deciduous or semi-evergreen, dioecious or monoecious. Branchlets never spinose, never corky or winged. Stipules 2, free, caducous, leaving a short transverse scar on each side of the leaf base. Leaves alternate, distichous or in several ranks; papery to leathery, margin serrate or entire. Flowers appearing at same time as leaves, unisexual. Male inflorescences cymes. Female inflorescences 1-flowered. Male flowers: perianth 4-or 5-parted, tepals imbricate. Ovary absent or inconspicuous and hair-shaped. Stamens equal in number to tepals; filaments erect or apically incurved; anthers oblong. Female flowers: perianth 4-or 5-parted, tepals narrow and ± imbricate. Drupes ovoid to ± globose; exocarp ± fleshy; endocarp bony. Seed with thin endosperm or not; embryo involute; cotyledons narrow.
In Malesia mainly found in areas subject to a rather strong seasonal climate, on various types of soil in the coastal lowlands, hills, and gallery forests, 0-750 m, locally often abundant and forming dense thickets.In the north temperate and subtropical regions the species flower in April-May and drupes ripen in July-August. Tropical species produce flowers twice a year, viz around March-April and Sept.-Oct. and fruit ripens in June-July or Nov.-Dec.The deciduous or semideciduous habit, flush-wise mode of growth, structure, size, colour of the inflorescence and flowers suggest that pollination is affected by wind. The drupes which turn to a deep red colour when ripe are possibly dispersed by frugivorous birds.