Herb to 1.2 m high. Stems thinly pilose with arachnoid hairs. Leaves green above with very sparse multicellular hairs, white to grey-green below with arachnoid hairs; sessile glands abundant; petioles (of basal leaves) solid. Capitula arranged in terminal corymbs; peduncles 2.5–5 cm long; involucre broadly ovoid to globose, 17–26 mm diam. at anthesis excluding patent outer bracts; median involucral bracts erect, linear-deltate, 13–16 mm long, 1.2–1.7 mm wide at base, glabrous or with a few glandular hairs. Corolla tube 9.5–11 mm long; lobes 1.8–2.5 mm long. Anthers 3.7–4.5 mm long. Achenes compressed-obovoid, 6.9–7.3 mm long, rugose, with indistinct longitudinal furrows, brown. Pappus bristles 80–150, of differing lengths, to 3.5 mm long.
A tall growing herb or shrub which takes two years from planting to flower and seed production. Plants can be 2 m tall. The plant forms a clump of very large, grey-green wavy-edged leaves. The leaves can be 50 cm long. The leaves and stems are covered with fine hairs. The leaves are paler underneath. In the second year a tall branched flower stalk 2 m tall grows from the centre of the clump. There are many flowers which are small and purple or white. They have a bract around them that is longer than the flower. The fruit is a spiky seed pod. This burr attaches itself to clothes. The burdock roots are long and slender and resemble parsnips. They can be a metre long and 3 cm wide. The skin is brown and the flesh is white.
Plants to 100–300 cm. Basal leaves: petioles solid, 15–36 cm, glabrous or thinly cobwebby; blades 25–80 × 20–70 cm, coarsely dentate to subentire, abaxially thinly gray-tomentose, adaxially green, sparsely short-hairy to nearly glabrous. Heads usually in corymbiform clusters, long-pedunculate. Peduncles 2.5–6 cm. Involucres 25–45 mm diam. Phyllaries linear to linear-lanceolate, glabrous to loosely cobwebby, inner usually stramineous (sometimes purplish), margins with minute spreading or reflexed hairs. Florets 40+; corollas purple (occasionally white), 9–14 mm, glabrous. Cypselae light brown, often with darker spots, 6–7.5 mm; pappus bristles 2–5 mm. 2n = 32 (Japan), 34 (China), 36 (Japan); (Sweden).
Plants openly branched, 1-1.5 m tall. Stems grooved, glabrous or with cobwebby eglandular and subsessile glandular hairs. Basal lvs broadly deltoid to ovate, green and sparsely hairy above, whitish and densely felted beneath, (15)-20-40 × (15)-20-35 cm; base truncate to cordate; apex subacute to obtuse; margin dentate with apiculate vein endings; petioles solid. Upper lvs similar to basal, becoming smaller. Infl. corymbose; peduncles (3)-4-9 cm long. Capitula (15)-20-25 × (20)-30-40 mm. Involucral bracts straw yellow or yellow-green, glabrous or with sparse cobwebby hairs; margins smooth. Florets c. = involucral bracts; corolla reddish purple. Achenes 6-7 mm long; pappus 1.5-3.5 mm long.
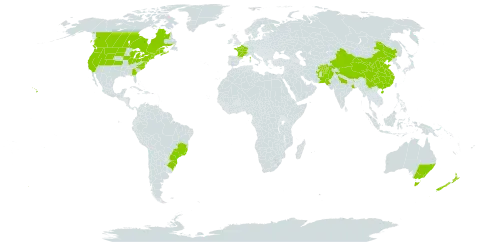
To 1.5 or even 3 m; lvs petiolate, the petioles mostly solid, progressively shorter upwards, the blade ovate or broader, cordate, to 5 × 3 dm, thinly tomentose beneath, subglabrous above; infl corymbiform, with long, glandular or glandular-hairy peduncles commonly 3–10 cm; heads large, the invol (2.5–)3–4 cm wide, generally equaling or surpassing the fls, glabrous or slightly glandular, and often with a few long cobwebby hairs; achenes 6–7 mm; 2n=32, 36. Native of Eurasia, sparingly established as a weed along roadsides and in waste places over most of the n. U.S. and adj. Can. Aug.–Oct.