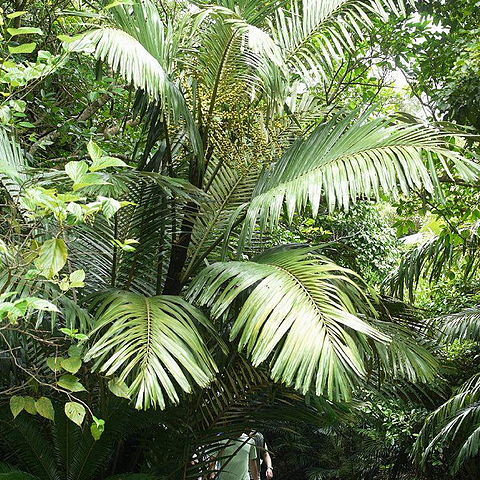
Stems clustered, to 4 m tall, 10-15 cm in diam. Leaf petioles to 1.8 m; rachis to 3 m; pinnae 38-41 per side of rachis, linear, very briefly lobed along margins, without ears at bases, regularly arranged and spreading in same plane except for basal few pinnae; middle pinnae 43-49 cm, ca. 2 cm wide at mid-point. Inflorescences to 60 cm; male rachillae many, 9-27 cm; male flowers 8-14 mm; sepals 2-3 mm; petals 9-14 mm; stamens 25-37; female rachillae many, 27-32 cm; female flowers ca. 3 mm; sepals ca. 2.5 mm; petals ca. 3 mm. Fruits orange or red, globose, ca. 1.5 cm in diam.