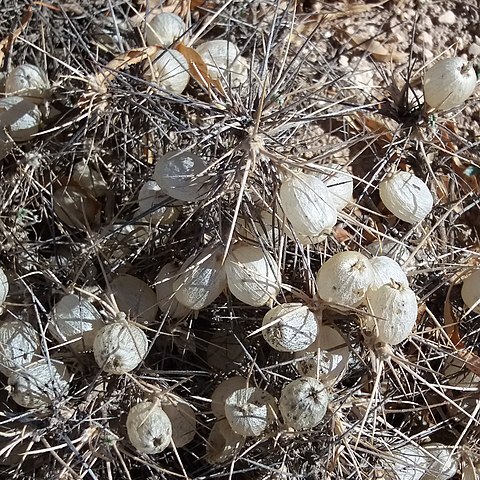
A perennial, or perhaps sometimes biennial, herb. Stems cylindrical with many faint ribs, usually glabrous or nearly so. Leaves up to 25 cm long, with 11-51 leaflets; stipules large, leaf-like, broadly triangular-ovate, acute with entire margins, free from the petiole; rhachis usually nearly glabrous, sometimes pubescent, always with a few hairs on and at the base of the petiolules; leaflets opposite or subopposite, narrowly elliptic or lanceolate, obtuse, up to 3 cm long and 14 mm wide, usually glabrous above, always with a few hairs on the midrib and margins beneath, sometimes pubescent. Racemes many-flowered, pedunculate, the rhachis nearly glabrous or pubescent, sometimes with blackish hairs; bracts whitish, linear, 1-2 mm long; bracteoles absent; pedicels white, brown or blackish pubescent, 2- long, reflexed after flowering. Calyx rather persistent, glabrous or with appressed white, brown or blackish hairs, oblique, the tube 1.5 mm., the upper teeth triangular, 0.5 mm., the lower teeth lanceolate, 1-2 mm long. Corolla purplish, white or yellow, 8-13 mm long, the standard and wings somewhat exceeding the keel or about the same length. Filaments whitish, rather persistent. Ovary stipitate, almost completely divided lengthwise, with 3-8 ovules on each side, shortly black pilose or more often glabrous. Pod lanceolate, somewhat curved, up to 4 cm long (including the stipe) and up to 7 mm wide, glabrous or, less often, shortly brown strigulose, conspicuously veined, the lower but not the upper suture impressed, usually rather papery, usually splitting lengthwise into 2 halves at maturity.
A herb. It has an erect stem about 1 m high. There are a few branches. The leaves are compound. They are 1-3 cm long. There are 10-15 pairs of leaflets. The flowers are bright yellow. They are in large groups. The pods are small and papery.