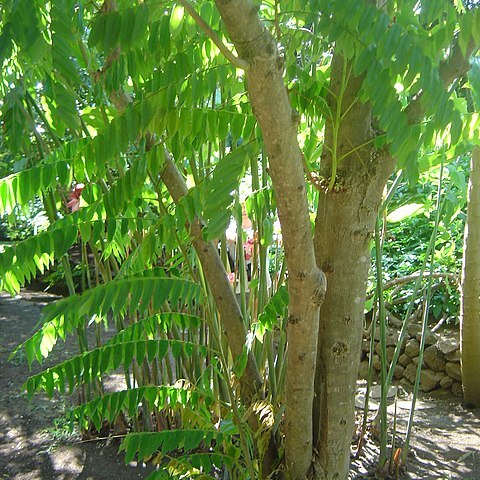
Small to large branched trees. Leaves imparipinnate. Inflorescences of cymes united in racemes, then in fascicles or pseudopanicles, axillary or cauliflorous; bracts and bracteoles subulate, caducous. Flowers heterostylous; sepals shortly connate at the base, imbricate; petals hypogynous, contorted, free or connate near the middle; stamens 10 (5 + 5) or 5 fertile and 5 staminodes; ovary 5-lobed, the carpels 2-7 ovuled. Berries indehiscent; seeds 2-several in each carpel, the endosperm fleshy, the outer tegument present or absent.
Trees or shrubs. Stipules absent. Leaves alternate or subopposite, odd-pinnate; leaflets nearly opposite. Inflorescences axillary or rameal, cymes or panicles. Flowers small or medium-sized, fragrant. Sepals red, semifleshy, basally connate. Petals white, pink, or purple, contorted. Stamens all fertile or 5 without anthers. Ovary several ovules per locule. Fruit a berry, oblong, usually 5-lobed. Seeds few or numerous, naked or arillate.