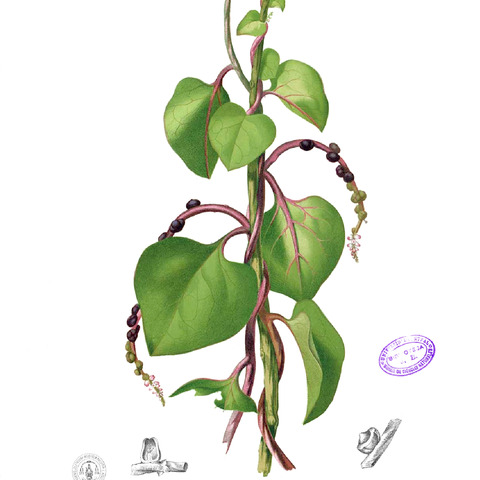
Vines [herbs], perennial, succulent, mucilaginous, glabrous. Leaves alternate, sessile or petiolate; blade margins entire [toothed]; stipules absent. Inflorescences axillary or terminal, racemose, [spicate, or paniculate], bracteate. Flowers usually bisexual, sessile or pedicellate, subtended by 1-2 bracts; perianth hypogynous, hypanthium present; sepals 2, distinct or basally connate; petals [4-]5[-13], basally connate; nectary annular; stamens [4-]5[-9], epipetalous, basally connate; filaments erect or reflexed in bud, broadened at base; anthers [basifixed]versatile, 4-locular, dehiscence longitudinal [terminal]; pollen [6-] panto-porate; pistils 3-carpellate, unilocular; placentation basal; ovule 1; styles 3, basally connate; stigmas slender, bifid to clavate or capitate [or style 1, with stigma capitate to 3-lobed]. Fruits utricles, surrounded by dry or fleshy perianth, winged or not. Seeds usually rust colored, testa membranous; endosperm copious; embryo curved.
Subsucculent, glabrous, twining herbs with slender stems and alternate, entire, petiolate or rarely sessile, exstipulate leaves. Flowers regular, hermaphrodite or unisexual, in spikes, racemes or panicles; bracts small; bracteoles 2–4, often 2 adnate to the base of the perianth, sometimes wing-like. Perianth 5-lobed; lobes imbricate, sometimes coloured, united into a tube below or almost free, persistent. Stamens 5, opposite to the perianth-lobes, inserted at their base; filaments free, short; anthers versatile, variously dehiscing. Ovary superior, 1-locular; ovule solitary, basal, shortly stalked, campylotropous; style terminal, simple or 3-fid, or 3 free styles. Fruit indehiscent, surrounded by the persistent often fleshy perianth or winged bracteoles. Seeds solitary, almost spherical; endosperm copious or almost absent, surrounded by the spirally twisted or semi-annular embryo
Vines herbaceous or herbs twining, usually fleshy, glabrous. Leaves simple, alternate, usually petiolate, margin entire. Inflorescences of spikes, racemes, or panicles; bracts 3, caducous; bracteoles 2, persistent. Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, small. Perianth segments 5, white or reddish, distinct or connate at base, imbricate in bud, persistent in fruit. Stamens 5, opposite to petals; filaments inserted on perianth. Ovary superior, 1-loculed; ovule 1, basal, campylotropous. Pistil united from 3 carpels. Style simple with 3 stigmas or 3 free styles. Fruit a utricle, dry or fleshy, often surrounded by persistent bracteoles and perianth. Seed globular; testa membranous; endosperm copious; embryo spirally twisted or semicircular to horseshoe-shaped.
Flowers small, actinomorphic, hermaphrodite or unisexual; bracts small; bracteoles 2–4, frequently appressed to base of perianth, sometimes winged
Flowers hermaphrodite, actinomorphic, in spikes, racemes or panicles; bracts small; bracteoles 2, often united to the base of the calyx
Stamens 5, inserted opposite and at the base of the sepals; filaments free, short; anthers with 2 parallel cells opening longitudinally
Ovary superior, 1-celled, with a solitary basal shortly stalked ovule; style terminal, often deeply divided into 3 stigmas
Seed solitary, almost spherical, with a membranous testa; endosperm copious, surrounded by the spirally twisted embryo
Ovary superior, unilocular; styles terminal, free or united or 3-fid; stigmas 3; ovule solitary, basal, short stalked
Stamens 5, inserted opposite and at base of perianth lobes; filaments free; anthers dehiscing variously
Sepals 5, often coloured, almost free or united into a 5-lobed tube, imbricate, persistent in fruit
Perianth 5-lobed, lobes united at base only or into a 5-lobed tube, imbricate, persistent in fruit
Twiners with slender steins and rather fleshy alternate entire petiolate leaves; stipules absent
Leaves alternate, entire or almost entire, usually petiolate, exstipulate
Fruit indehiscent, enveloped by persistent frequently fleshy perianth
Inflorescences of spikes, racemes or panicles, axillary or terminal
Fruit indehiscent, surrounded by the persistent often fleshy calyx
Subsucculent herbs with slender twining stems, glabrous
Seeds solitary, globose; endosperm present
Petals absent