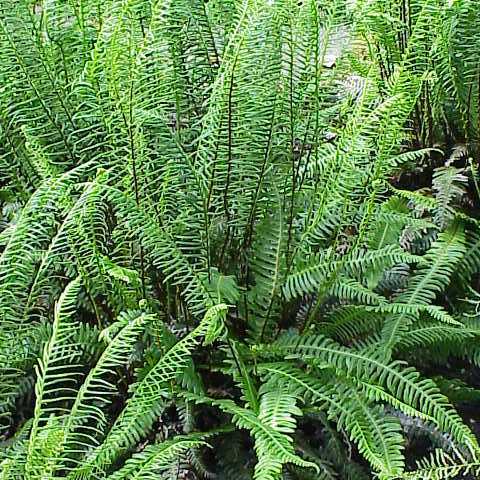
Plants mostly terrestrial, sometimes tree ferns (like small trees), rarely scandent. Rhizome mostly erect, or creeping or scandent, usually dictyostelic (Stenochlaena meristelic), scales brown, entire. Fronds monomorphic or dimorphic, mostly long stipitate; stipe with 2 to several vascular bundles, scaly at base; lamina pinnate, pinnatifid, or bipinnatifid, rarely simple, thickly papery to leathery, glabrous or usually with small scales; pinnae rarely articulate to rachis (Stenochlaena); veins free or anastomosing with 1 or more series of areoles, without included free veinlets. Sori elongate or continuous along vascular network or commissure on either side of midrib, indusiate, rarely exindusiate, rarely acrostichoid; indusium facing toward costa or costule; annulus longitudinal, interrupted. Spores elliptic, bilateral, monolete.
Terrestrial and lithophytic ferns with erect creeping or sometimes scandent scaly rhizomes. Fronds often dimorphic. Young fronds often red. Lamina usually pinnatifid, pinnatisect or pinnate, sometimes simple or lobed, with narrow linear fertile pinnae or pinnules in some species; veins free, or anastomosing into 1 or more rows of areoles on either side of costa. Sori elongate, in 2 rows on either side of costa, often covering the lower surface of fertile pinnae (if narrow), or short in 1 or more longitudinal rows attached to veinlets parallel to costa; indusium (present in all genera except Stenochlaena ) opening towards costa. Spores monolete, bilateral.
Usually terrestrial ferns, sometimes lithophytic, epiphytic or climbing. Rhizomes erect to long-creeping, scaly, scales not clathrate
Rhizome forming an erect trunk or wide–climbing, scaly at apex