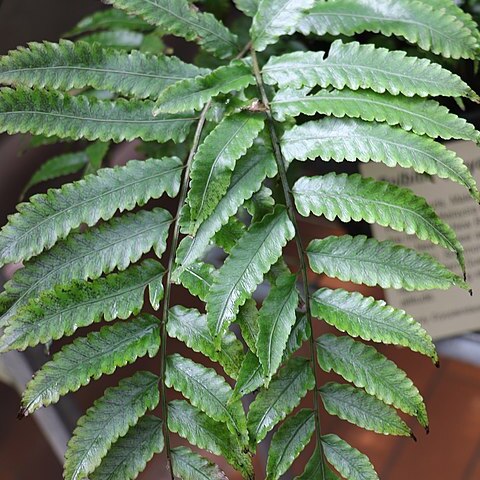
Sterile fronds pinnate, up to 130 cm long; lamina index 1-3(-4), up io 80 by 40 cm, terminal segment 9-26 cm long, herbaceous to subcoriaceous, green or brown (or blackish); pinnae 13-52, index 2-7, 7-22 by 1.3-3.5(-4.5) cm, base symmetrical, (narrowly to) broadly cuneate to cordate, margin usually lobed 1/3-⅔ towards the costa, sometimes either ± entire or lobed to 4/5 towards the costa, with a usually rather inconspicuous spine in the sinuses, apex acute to acuminate, lobes close together to spaced, straight or subfalcate, margin entire or crenate-serrate; terminal segment narrowly triangular, shorter than the remaining part of the lamina; venation pattern: veins forming a regular network, areoles angulate isodiametric or elongate decreasing in size towards the margin, see Fig. 31j-k. Fertile fronds up to 120 cm long; lamina index 3-6, pinnae index 5-15, 3-15 by 0.4-1.7 cm. Sporangia usually inserted all over the lower surface, sometimes situated along the margin only, the arrangement usually acrostichoid, sometimes ± pteridoid. Spores with a smooth cristate perispore. Chromosomes n = 41, 2n = 82, 123.
More
Rhizome short-creeping; scales narrowly ovate with narrowly acute apices. Fronds erect, 30–120 cm long, dark green to dark bluish green. Stipe 15–50 cm long, scaly. Lamina 1-pinnate, with a pinnatifid apex. Pinnae of sterile fronds attached by stalks only except for 1 or 2 pairs immediately below the apex, 8–20 cm long, 2–4 cm wide; longest pinnae towards the base; margins shallowly to deeply lobed. Fertile laminae with smaller narrower paler pinnae and a longer stipe. Veins anastomosing, with several series of areoles on each side of a pinna midrib. See also Short et al. (2003: 66).
In Queensland common in lowland rainforests, and up to 500 m altitude (Jones 1998: 431). In the Northern Territory, with only a few records, found on shaded rock faces and overhangs along perennially wet creek (Short et al. 2003: 66).
More
On rocks and in soil in rain-forest, mostly near streams; several times reported from limestone; 0-1200(-1700) m.