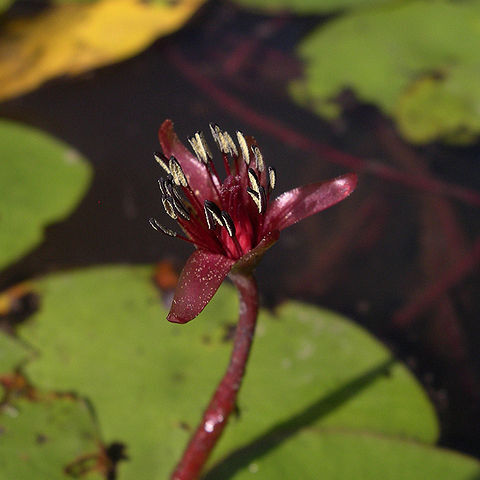
All submerged parts with jelly-like mucilage. Leaves: petiole to 2 m long; lamina orbicular to elliptic, 2.5–11.5 cm long, 2–7.5 cm wide, green above, reddish brown or purplish beneath. Flowers held at or slightly above water surface. Sepals 9–14 mm long, 3–6 mm wide, purplish red or brownish red. Petals 12–18 mm long, 3–4 mm wide, purplish red or brownish red. Filaments to 10 mm long; anthers reddish, c. 3.5 mm long. Fruiting carpels to c. 10 mm long. Seeds 2.5–3 mm long.
A water plant. It is a herb. It has runners or stolons and underground stems or rhizomes. It keeps growing from year to year. It forms roots at the nodes. The leaves float. The leaf stalk join to the centre of the leaf. The leaves are 5 cm long and 8 cm wide. The leaf stalk is up to 2 m long. The stems, leaf stalks and leaves under the water have a slimy covering. The leaves are often red underneath. The flowers occur singly. They are in the axils of leaves and they float.
Stems to 1--2 m, glabrous, base rhizomatous. Petiole 25--40 cm; leaf blade 5--10 × 3.5--6 cm, glabrous. Flowers 1--2 cm in diam.; peduncle 6--10 cm. Perianth dull purple; segments 10--15(--20) × 2--7 mm; petals slightly longer and narrower than sepals, apex obtuse. Stamens 1/2 as long as petals, anthers linear, ca. 4 mm. Fruit 6--10 mm. Seeds 1--2, 2.5--4 × 2--3 mm. Fl. Jun., fr. Oct. 2n = 72, 80.
Leaves floating, rotund, peltate, 7.5 (10) x 5–7 cm., margin entire, green above, reddish-brown or purplish below, nerves 12, radiating from the apex of the petiole, rather faint, petiole reddish-brown, attached at the centre of the leaf-blade, up to 1 m. or more long according to the depth of the water, c. 1.5 mm. in diam.
Stem to 2 m; lf-blades elliptic, 4–12 cm, half as wide; fls dull purple, on stout peduncles to 15 cm; sep and pet persistent, the latter 12–16 mm, the former somewhat shorter; 2n=80. Quiet water; N.S. and e. Que. to Minn., s. to Fla. and Tex.; also on the Pacific slope, and in tropical Amer., and the Old World. Summer.
Leaf blade 3.5-13.5 × 2-8 cm. Flowers ca. 2 cm diam.; perianth parts dull purple, 10-20 × 2-7 mm; petals slightly longer and narrower than sepals. Fruits 6-10 mm. Seeds 1-2, 2.5-4 × 2-3 mm. 2 n = 80.
Glabrous, aquatic herb. Submerged parts of plant covered with profuse, clear, slimy mucilage. Leaves floating, peltate. Flowers produced under water, purplish to brownish red.
Stamens with slender papillose filaments up to 1 cm. long; anthers reddish, 3.5 mm. long, narrowly oblong, apiculate at the apex.
Carpels 5 x 2 mm., narrowly lanceolate-ovoid, sparsely papillose, stigma simple, 3 mm. long, papillose.
Glabrous aquatic plant with all its submerged parts covered with a profuse, clear, slimy mucilage.
Flowers solitary, axillary on reddish-brown peduncles up to c. 8 cm. long, c. 2 mm. in diam.
Sepals purplish-brownish-red, petaloid, c. 1.4 x 0.3 cm., narrowly oblong, apex rounded.
Ripe carpels 7 x 2 mm., ellipsoid with a persistent stigma.
Seeds 3.5 x 2.3 mm., ellipsoid, testa pale brown.
Petals similar to the sepals but slightly larger.