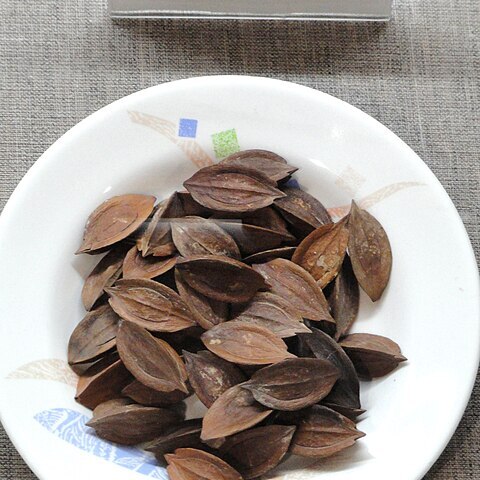
Trees, up to 25 m tall, ca. 1.2 m d.b.h. Branchlets 1-1.5 cm in diam., sparsely gray pubescent when young; top bud yellow pubescent. Leaves stipulate; stipules subulate, pubescent, early deciduous; leaflets 6-8(-10) pairs; blades oblong or obovate-lanceolate, 10-20 × 4.5-6 cm, adaxially glabrous, abaxially pubescent, base rounded, margin sinuate or entire, apex acuminate with acumen 10-15 mm; lateral veins 18-25 pairs. Inflorescences axillary, cymose panicles in male plants, 30-40 cm, nearly glabrous, branches 3-4 cm. Calyx ca. 2 mm. Stamens glabrous; filaments united for ca. 1/2 of length; disk tubular, 1.5-1.8 mm high, margin and abaxial surface hirsute in male flowers, annular, 3-fid, fimbriate in female flowers. Infructescences extra-axillary or axillary, 5-8 cm, 1-3-fruited; persistent calyx disk-shaped, shallowly 3-lobed, ca. 10 mm in diam. Drupe green, spindle-shaped, 3-ribbed, 4.5-5 × 1.8-2 cm, glabrous, or obovoid and 3-or 4-ribbed, apex acute, truncate or excavated; stigma persistent; cross section of pyrene acutely triangular or rounded. Fr. Jul-Oct.
More
A large tree which loses its leaves during the year. It grows 10-20 m high and has a trunk 45-55 cm across. The trunk is straight and branches after 10 m height. The bark is grey and not cracked but can split. The young branches are green and wrinkled along their length. The leaves are made up of 8 or 9 pairs of leaflets with one at the end. The leaves are 25-37 cm long and the leaflets are 7-9 cm long by 3-3.5 cm wide. They are dark green on the upper surface and paler underneath. The base of the leaflets is rounded while the tip is pointed. There are 10-11 pairs of veins. The flower clusters occur near the ends of branches. These are 15-17 cm long. The fruit is 3 cm long by 1.5 cm across and triangular in cross section. It is green with the middle layer 2.5-3 mm thick. The seed is hard.
A tropical plant. It grows on humus rich soils. It occurs below 300 m altitude in Vietnam. It needs plenty of sunlight. It is native of the eastern Himalayan region. In Sikkim it grows below 500 m above sea level. In southern China it grows between 400-1,300 m above sea level. In Yunnan.
More
Mixed forests at elevations of 400-1,300 metres.