Tree (3-)10-30(-44) m by 20-70(-100) cm, sometimes buttressed. Branchlets 0.25-1 cm thick, glabrescent; pith with some large to many small vascular strands, all or part of them peripherally arranged. Stipules caducous, inserted on the branchlet near the base of the petiole, reniformous, 5 by 4 mm, with various intergrades to: subpersistent and inserted on the base of the petiole, semi-rotundate, 17 by 12 mm, margin repandous; nearly always tomentose. Leaves (0-)2-6-jugate, 17-60 cm long, glabrous to tomentose. Leaflets ovate to oblong-lanceolate, 3-27 by 1-9 cm, chartaceous to coriaceous, smooth to bullate, glabrous — sometimes waxy white beneath — to densely tomentose beneath and on the midrib above; base cuneate to faintly cordate, slightly inequilateral; margin entire to dentate or serrulate; apex (gradually to) rather abruptly shortly acute-acuminate, acumen mostly dentate or serrate; nerves 9-22 pairs (angle 60-90°, gradually decreasing from base to apex), slightly curved, often partly arching near the margin. Inflorescences terminal, sometimes with additional ones in the upper leaf-axils, paniculate (male) to subracemose (female), 5-40 cm long, often densely reddish-brown tomentose, sometimes glabrous. Bracts concave. Flowers 8-13 mm long, outside densely ferrugineously pubescent. Calyx 4-9 mm high. Stamens 6, filaments glabrous, in ♂ flowers often slightly connate, adnate to the disk, in female flowers inserted on the rim of the disk. Disk in ♂ flowers from globular, solid, tapering into a style-like appendix, to cupular, thick-fleshy, without any rudiment of the pistil; 1-3 mm high, nearly always glabrous; in female flowers minute, faintly 6-undulate, glabrous to tomentose. Pistil glabrous or pilose. Infructescences 5-25 cm long, densely tomentose, with 1-6 fruits; calyx funnel-shaped, triangular, c. 8 mm diam., to: flat, orbicular, 1.5 cm diam., with undulate margin. Fruits ellipsoid (to obovoid), rounded triangular in cross-section, 4.5-7 by 1½-3 cm, sparsely pilose to glabrous; pyrene smooth, acutely triangular in cross-section; lids 2-4 mm thick. Seeds 1-2, sterile cells moderately reduced.
More
A tree. It grows 30 m high. The young branches have red hairs. The leaves have 3 pairs of leaflets. They are broadly oval. The young leaflets are finely hairy at least on the veins. The leafy structures (stipules) at the base of leaf stalks only occur on very young branches and then fall off. They are kidney shaped. The leaves are narrowly oval and leathery. They have wavy edges. The flowers are yellow to red. The fruit is oblong and 3.5-6.5 cm long by 1.5-3 cm wide. It is pale green and fleshy. The fruit are oval and green. The kernels are small and the shells are hard. These stones are 3 angled.
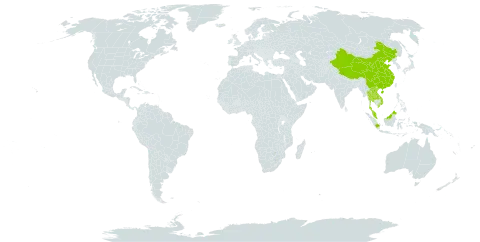
Secondary forest, especially on periodically flooded sandy alluvium. Rain-forests, on dry or swampy soils, under everwet or subseasonal conditions, mostly at low elevations, rarely to 2,000 metres.
More
Rain-forests on dry or swampy soils, under everwet or (in E. Java) subseasonal conditions, mostly at low altitudes, rarely up to 2000 m. Fl. Mainly Nov.-Apr.; fr. Mainly May-Sept.
A tropical plant. It occurs in lowland mixed forest normally below 800 m altitude. It can be up to 1,200 m above sea level.