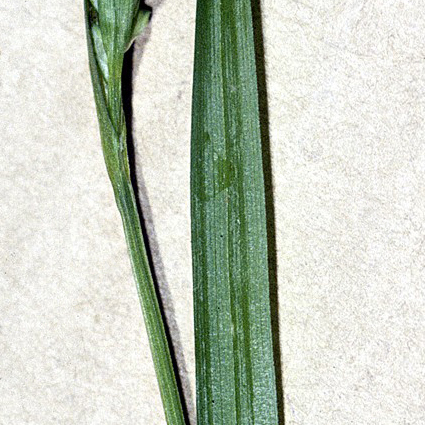
Culms densely tufted, ascending, lax or, occasionally, decumbent, 12–44 cm × 0.7–1.2 mm. Leaves: basal sheaths brown; sheaths 3–24 mm, serrulate; blades ascending, midrib well developed abaxially, lateral veins developed, flat, 10–32 cm × 3–10 mm, blades of overwintering leaves smooth. Inflorescences: peduncles of proximal spike 0–8 cm, distal lateral spike not exserted; of terminal spike to 0.2 cm. Bracts 10–30 × 2–7 mm, 2d pistillate bract frequently overtops terminal and distal lateral spike, blade of distal lateral spike linear, narrower than spikes, widest bract blade of distalmost lateral spike 0.5–3.4 mm wide. Spikes 4(–5) per culm; lateral spikes 9–22 × 2.8–4 mm; terminal spike linear, 7–16 × 1.2–2 mm, arising from same bract as distal lateral spike, usually surpassed by distal bract. Pistillate scales 2–2.5 × 1–1.8 mm, apex acute or apiculate. Staminate scales ovate, 2.2–2.6 × 0.8–1 mm, margins hyaline or slightly brown tinged, apex acute. Anthers 1.6–2 mm. Perigynia 5–14 per spike, overlapping or slightly scattered on proximal spike, ascending or spreading, 8–18-veined, 2–3 veins conspicuous, others obscure, elliptic-obovate, 2.2–3.2 × 1–1.5 mm, membranous; beak abruptly to slightly curved, 0.3–1.1 mm. Achenes obovoid, 1.8–2.8 × 0.8–1.2 mm. 2n = 36.
More
Tufted, 2–6 dm; basal sheaths brown; largest lvs to 10 mm wide; upper bract-sheaths minutely serrulate on the angles; terminal spike staminate, 0.7–1.6 cm, sessile or on a short peduncle to 2 mm, surpassed by or only slightly surpassing the uppermost pistillate spike; pistillate spikes 2–4(5), 1–2 cm, the upper 1 or 2 approximate to the staminate one, sessile or short-peduncled, the others more remote, evidently pedunculate, none basal; second pistillate bract often overtopping all the spikes; pistillate scales usually short-awned or apiculate; perigynia 5–14, 2.2–4.1 mm, 2-ribbed, otherwise nerveless or only obscurely few-nerved, obovoid and obscurely trigonous, abruptly contracted to the short, entire beak; achene trigonous; 2n=36. Moist woods; Nf. to ne. Minn., s. to N.J., Pa., Ind., and Wis., and in the mts. to N.C. and Tenn.