A medium sized tree. It grows to 24 m high. The trunk can be 50 cm across. The trunk is long and branch free. The limbs are spreading and the crown is round. The bark is grey or pale brown and smooth. It gradually develops narrow cracks. The leaves are 12-20 cm long with 7-11 leaflets along it. The leaflet at the end is about the same size as the last pair. The leaflets get smaller towards the base or the leaf stalk. The leaflets are slightly curved and have fine teeth. They are shiny and dark green on top and paler, hairy and with small dots underneath. They turn yellow in autumn, The male and female flowers are separate. The fruit have irregular lines along them when young. The fruit are broadest at the tip. They are 20-35 mm long. They occur either singly or in pairs. The nuts are small, rounded and thin shelled. They can be cut with a knife. The kernel is reddish-brown and bitter.
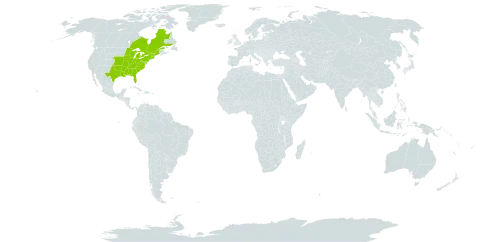
Bark scaly; winter-buds bright orange-yellow; lfls mostly (5)7–9(11), the lateral lanceolate to lance-ovate or elliptic, the terminal commonly long-cuneate at base and sessile or nearly so; staminate catkins clustered just beneath the new growth on the wood of the previous year’s twigs; fr obovoid to subglobose, often somewhat flattened, 2.5–3.5 cm, winged chiefly above the middle, splitting to about the middle; nut subglobose to obovoid, 1.5–3 cm, at least two-thirds as thick; obscurely angled, otherwise smooth, tipped with a slender, persistent point; kernel bitter; cotyledons bifid; 2n=32. Woods; s. Me. and sw. Que. to Minn. and e. Neb., s. to Fla. and Tex. C. ×laneyi Sarg. is a hybrid with C. ovata.