Lianas, woody. Branchlets terete, with longitudinal ridges, sparsely pilose; tendrils bifurcate. Leaves pedately 5-foliolate; stipules brownish, ovate-lanceolate, 3-4 × 1.5-3 mm, membranous, sparsely pilose; petiole 5.5-16 cm; central petiolule 1.5-5 cm, lateral petiolules 2-4 cm, petiolules of lateral leaflet complex 1-3.5 cm, sparsely pilose; leaflets abaxially pilose, adaxially with appressed hairs, lateral veins 6-11 pairs, veinlets inconspicuously raised; central leaflet obovate-elliptic; lateral leaflets ovate-elliptic, 5-22 × 2.5-9 cm, base nearly truncate, rounded, or slightly cordate, margin with irregular teeth, apex caudate-acuminate. Corymbose polychasium axillary; peduncle 15-16 cm, with nodes, pilose. Pedicel 2-3 mm, densely pubescent. Buds oval, 2-2.5 mm, apex rounded. Calyx saucer-shaped, pubescent, entire. Petals ovate-elliptic, 1.7-2.2 mm, nearly glabrous. Anthers ovoid-elliptic, poorly developed in female flowers. Disk well developed, margin undulate. Lower part of ovary adnate to disk; style slender; stigma slightly expanded, or cylindrical in male flowers. Berry elliptic, 1.2-1.5 cm in diam., 2-or 3-seeded. Seeds semiglobose, base rounded, apex subrounded, rostrum inconspicuous, upper raphe narrow, surface smooth, ventral holes nearly rounded, 3-5 mm in diam. Fl. Jun, fr. Sep-Nov. 2n = 80.
More
A vine. It has tendrils that enable it to attach to other plants. The leaves are simple and alternate. The leaf stalks are 7-13 cm long. The leaves are 7-15 cm long by 4-7 cm wide and have 5 leaflets or lobes.
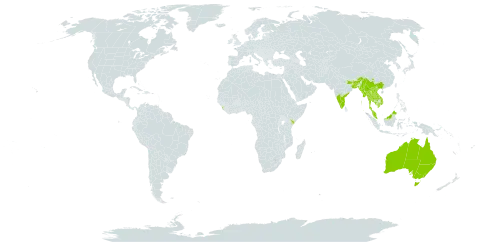
Common in shrubberies, hedges and waste places throughout various parts of its range. Forests, shrublands, rocky areas, roadsides; at elevations from 800-2,200 metres in China.
More
It is a subtropical plant. It occurs in the Western Ghats in India. It grows between 800-2,200 m above sea level in China.