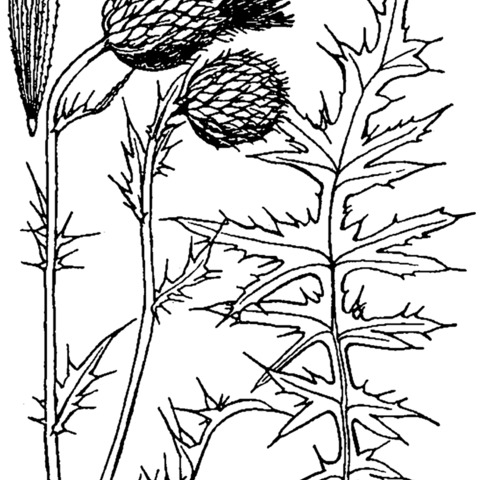
Perennials 30–140 cm; horizontal runner roots that produce root sprouts. Stems 1–several, erect, gray. or white-tomentose; branches 0–few, ascending. Leaves: blades oblong-oblanceolate to narrowly elliptic, 4–40 × 1–10 cm, bases usually not decurrent, finely spiny-toothed and undivided to coarsely toothed or deeply pinnatifid, lobes broadly triangular to linear-lanceolate, often revolute-margined, main spines 1–7 mm, abaxial faces white-tomentose, adaxial faces green, thinly tomentose, ± glabrate; basal usually absent or withered at flowering, winged petiolate; principal cauline proximally winged-petiolate, distally sessile, well distributed, gradually reduced, bases usually not decurrent; distal cauline well developed. Heads erect, borne singly and terminal on main stem and branches, or few in corymbiform arrays from distal axils (not subtended by ring of spiny-margined bracts ). Peduncles 0–5 cm (elevated above distal leaves). Involucres ovoid to broadly campanulate, 2–3.5 × 2.5–3.5 cm, thinly arachnoid. Phyllaries in 7–12 series, strongly imbricate, greenish with subapical darker central zone, ovate or lanceolate (outer) to linear (inner), abaxial faces with prominent glutinous ridge; outer and middle entire, bodies appressed, entire, acute, spines abruptly spreading, slender, 2–4 mm; apices of inner spreading, flexuous, narrow, flattened, finely serrulate, ± scabrous. Corollas purple (white), 23–36 mm, tubes 12–15 mm, throats 6–8.5 mm, lobes 5–9 mm; style tips 4–7 mm. Cypselae light brown, 3–5 mm, apical collars stramineous, 0.5–1 mm; pappi (white or tawny. 20–30 mm. 2n = 22, 24.
More
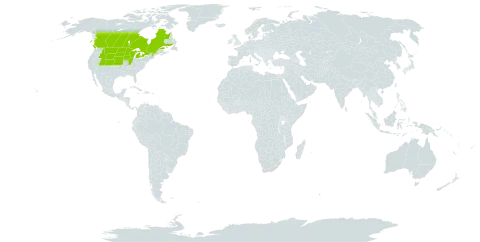
Resembling no. 10 [Cirsium undulatum (Nutt.) Spreng.], but smaller and more delicate, 3–8 dm, and vigorously spreading by short-lived creeping roots, the individual plants thus established generally becoming taprooted; lvs usually rather deeply pinnatifid, the lobes commonly lance-triangular and seldom over 7 mm wide, or sometimes fully as wide as those of no. 10, varying to subentire and merely spiny-margined (especially the basal ones); heads merely rounded (not invaginated) at the base, and avg smaller, the invol 2–2.5(–3) cm, its bracts appearing darker, narrower, more numerous, and more closely imbricate, their spine-tips sometimes under 3 mm; fls rich purple (white); achenes 3–5 mm, with a conspicuous apical yellow band; 2n=22. Swales and other moderately moist, poorly drained sites on the Great Plains, extending e. to Man., Minn., and Io., and occasionally intr. eastward. June–Sept. (C. canescens, misapplied)