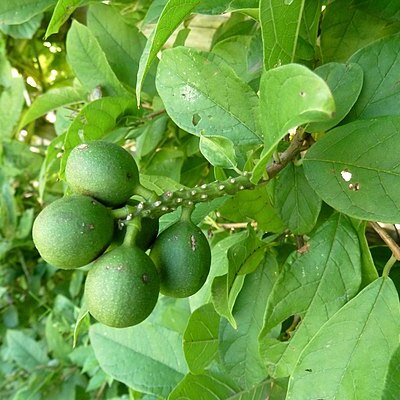
A coppicing semiscandent or scandent shrub 2-8 m tall, branches at first puberulous, later glabrescent, some sparingly armed with straight or recurved petiolar spines up to 15 mm long; bark smooth, fulvous, later finely longitudinally striate-reticulate, fuscous. Leaves opposite, ternate, verticillate or alternate, exstipulate, petiolate; petioles ± 4-7(-15) mm long, green, puberulous or, on distal tendrillar shoots up to 25 mm long, geniculate, brown, sometimes persisting as blunt, woody spines; lamina papyraceous, elliptic to obovate with obtuse or cuneate base and acuminate apex, 25-70(-90) x 10-40(-50) mm, pellucid-punctate, sparsely puberulous above with admixed stalked glandular hairs, sparsely pilose below on nerves and with tufts of hair in nerve axils, margin ciliate; midrib depressed above, prominent below, lateral nerves 7-9 pairs. Inflorescences of congested racemes up to 60 mm long, terminal, and terminal on abbreviated lateral branches, or of short panicles. Flowers scarlet, pentamerous, actinomorphic, epigynous, shortly pedicillate, bracteate, bracts petiolate, leaf-like, or sessile, ovate-acute, 5-14 x 2-5 mm, green, caducous; pedicel green, puberulous, 1-2 mm long; lower hypanthium (enclosing and adnate to inferior ovary) green, puberulous with admixed stalked glandular hairs, 3.0-4.0 x 1.5-2.0 mm; hypanthial tube proximally cylindric, constricted above, distally broadly infundibuliform, proximal part ± 2 x 2 mm, distal part 4 x 5 mm, green, puberulous with admixed stalked glandular hairs outside, glabrous within. Sepals broadly triangular, acute, dull red, puberulous without and within, 2 x 2 mm. Petals obovate to spathulate, scarlet, minutely puberulous without with ciliate margin, glabrous within, 5.0-8.0 x 3.0-4.7 mm. Stamens 10, biseriate, exserted; filaments scarlet, 7-10 and 10-12 mm long; anthers red, dorsifixed, bithecate with longitudinal dehiscence, ± 1 mm long. Disc margin pilose, not free. Ovary inferior, unilocular with 2 pendulous anatropous ovules; style free, scarlet, ± 16 mm long with minutely capitate green stigma. Fruit a subglobose or ovoid, indistinctly 5-angled, 1-seeded, stipitate nut ± 23 mm in diameter; pericarp brown, glabrous; apical peg absent. Germination hypogeal.
More
Coppicing, scandent shrub, 2-8 m high, branches sparingly armed with petiolar spines up to 15 mm long, fuscous (brownish grey). Leaves elliptic to obovate, papyraceous, pellucid-punctate, sparsely pilose below on nerves, with tufts of hairs in nerve axils, margins ciliate; lateral nerves 7-9 pairs. Inflorescence a congested raceme, up to 60 mm long. Flowers scarlet, pentamerous. Flowering time Sept.-Apr. Fruit a 1-seeded nut, ± 23 mm in diam., subglobose or ovoid, indistinctly 5-angled, pericarp brown, apical peg absent.
It is a sturdy shrub, a rambler or a small tree up to 8 m tall. The leaves are simple and opposite. They are dull green above and lighter below. They are 3.5-10 cm long and oval. They have a point at the end. The flowers are bright red. They are in short dense clusters in the axils of leaves and at the ends of branches. They are small with leaf like bracts. The fruit is round or egg shaped. It is often slightly five angled. It is smooth and with one seed.