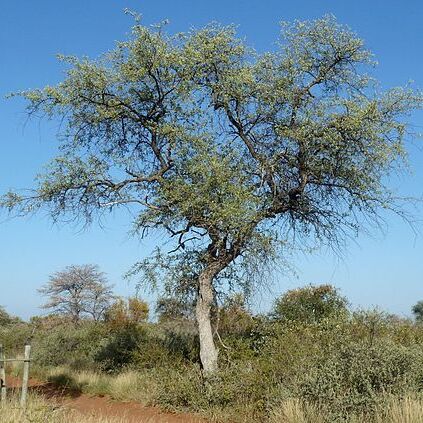
A tall tree which loses its leaves during the year. It can be 21 m tall. The trunk can be 1 m across. The bark cracks in rectangular flakes. The wood is very hard. The young branches and twigs often have hard spines. The leaves are simple and opposite. They are 2.5-4 cm long by 0.8-3.5 cm wide. They are oblong. The base is narrow and the edges are wavy. They are silvery grey and with red scales. The flowers are yellow in loose spikes in the axils of leaves and near the ends of branches. The fruit are 1.9 cm across and with 4 wings. They are yellowish-green but can have a red tinge.
Leaves silvery, opposite or sub-opposite; lamina 2·5–8·5 x 1–3 cm., papyraceous to subcoriaceous, narrowly elliptic to elliptic-oblong, densely silvery-lepidote on both surfaces otherwise glabrous, scales often contiguous or overlapping, apex obtuse or rounded and often mucronate, base obtuse to narrowly cuneate; lateral nerves 4–7 pairs, slightly prominent on both surfaces, usually without domatia; petiole 4–10 mm. long, lepidote but otherwise glabrous or almost so.
Inflorescences of spikes up to c. 10 cm. long, often forming a terminal panicle by suppression of the upper leaves, or unbranched lateral spikes up to 5 cm. long; rhachis lepidote, otherwise glabrous or sparsely puberulous; bracts absent or very caducous.
Lower receptacle 2·5(3) x 0·25–0·3 mm., densely silvery-or rufous-lepidote, otherwise glabrous or nearly so; upper receptacle little developed, almost flat when the flowers are mature, densely silvery-or rufous-lepidote, otherwise glabrous or nearly so.
Fruit 1·3–1·8 cm., subcircular to broadly ovate in outline, fairly densely to densely silvery-lepidote, apex pointed, apical peg very short (up to 0·5 mm.) to medium (1 mm.) or absent, wings up to 7 mm. broad, stipe 2–3 mm. long.
Scales 120–300µ in diam., roughly circular, cells very numerous and small (marginal cells c. 40–100), divided as in the sectional description; cells beneath the scales with conspicuous round papillae.
Tree, up to 15 m high. Branchlets spiny. Bark rectangularly reticulate. Leaves densely lepidote. Fruit 15 mm, silvery-lepidote. Flowers yellowish.
Tree up to 30 m. tall (usually 6–10 m.) or shrub; bark light-grey or whitish; branchlets often becoming spiny, glabrous.
Cotyledons 2, 15–18 x 15 mm., subcircular, with petioles 9–11 mm. long arising at or below soil level.
Flowers sessile, yellowish, densely lepidote but otherwise glabrous or nearly so.
Petals 1–1·2 x 0·4–0·6 mm., obovate to spathulate, glabrous.
Stamen-filaments 1·5–2 mm. long; anthers 0·3–0·4 mm. long.
Disk 2–2·5 mm. in diam., margin densely tomentose.
Sepals 1·5 x 1·5 mm., ovate-triangular.