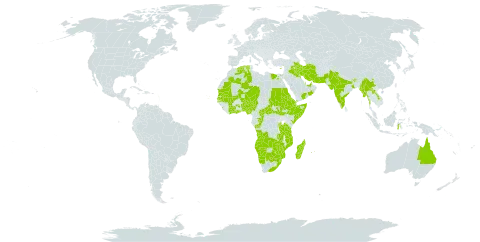
Annual herb to 1 m, rarely to 1.5 m; stems often purplish, covered with spreading setulose pubescence when young, on older stems pubescence confined to one side of stem.. Leaves narrowly elliptic to elliptic, ovate or lanceolate, 4–9(–12.5) cm long, 0.6–2.4 cm wide, margins coarsely serrate, with a pair of basal setae 0.6–10 mm long, rounded or broadly cuneate at the base, acute to subacute, with pubescence on midrib, pubescence beneath especially prominent on midrib and veins; petioles 0.7–1.9 cm long, covered with setaceous hairs; stipules up to 1 cm long, pubescent.. Inflorescence of 1–3-flowered cymes; bracts up to 3.3 mm long, ciliate; peduncles ± 1 mm long, lengthening in fruit; pedicels ± 1 mm long.. Sepals 4–5, 5.5–6.3 mm long, 1 mm wide, dorsal surface pubescent especially at base.. Petals 4–5, 5–7 mm long, 2–2.5 mm wide, obovate tapering to a short ciliate claw; stamens ∞; ovary cylindric, 3 mm long, shortly pubescent.. Capsule cylindric, torulose, 2.5–6.5 cm long, 1–2.5 mm wide, held erect, straight or slightly curved, splitting into 3, rarely 4, valves, glabrous when mature, covered with scattered stellate hairs especially when young.. Seeds oblong-ovoid, blackish and pruinose, up to 1 mm in diameter, smooth.. Fig. 18/12 (fruit, p. 103), 20 (p. 112).
Herbs annual or perennial, many branched, pilose. Stipule subulate; petiole 0.5-1 cm, pilose; leaf blade elliptic or ovate-oblong, 1.5-3 × 1-2 cm, hairy only on veins abaxially, glabrous adaxially, lateral basal veins 1/3 as long as leaf blade, base broadly rounded, margin crenate, apex obtuse. Cymes opposite to leaves, 1-3-flowered; peduncle very short. Sepals ca. 5 mm. Petals nearly spatulate, 5-6 mm. Stamens 15-20; filaments 5-6 mm. Ovary 3-loculed. Capsule 1-3-fascicled, long cylindrical, 5-7 × ca. 0.3 cm, apex beaked. Seeds separated by septum. Fl. Aug, fr. Sep.
Annual herb, 0.30-1.05 m high. Stipules setaceous, up to 10 mm long. Leaves lanceolate-oblong, apex subacute, base rounded, usually with a pair of basal, setaceous lobes, margins crenate-serrate. Inflorescences of 1-3-flowered cymes opposite upper leaves; peduncles ± 1 mm long, setose-pubescent. Flowers ± 5 mm long, yellow. Sepals narrowly lanceolate, 6-10 mm long. Petals as long as sepals. Androgynophore ± 0.5 mm long. Flowering time Dec.-May. Fruit a capsule, 25-70 mm long, 3-or 4-angled and-valved. Seeds many.
Leaf-lamina 2–12 × 0·5–3·5 cm., lanceolate to oblong or narrowly oblong, apex acute or subacute, margin crenate-serrate, usually with a pair of setaceous basal appendages, rounded or broadly cuneate at the base, glabrous or setulose-pilose on both surfaces especially on the nerves; petiole up to 2–5 cm. long when low down on the stems but usually rather shorter, with a spreading setulose pubescence especially on the upper side; stipules c. 1 cm. long, setaceous, setulose-pubescent.
Annual herb up to c. 1 m. tall, erect and branching or sometimes with decumbent branches if the main stem is cut down or browsed; branchlets often purplish and when young with a spreading setulose pubescence not confined to one side of the stem.
Capsule many-seeded, 2·5–7 cm. long, held erect, straight or slightly curved, 3–1-angled, 3–valved; valves scabrous and sometimes somewhat torulose outside, with a series of hollows inside fitting the seeds.
Inflorescences of 1–3-flowered cymes borne opposite the upper leaves; peduncles c. 1 mm. long but lengthening in fruit, setose-pubescent; pedicels similar, c. 1 mm. long.
Erect or sometimes decumbent annual herb, 1 m high. Capsules up to 70 mm long, held erect, valves minutely scabrous. Peduncles up to 2 mm long. Flowers yellow.
Sepals 6–10 mm. long, narrowly lanceolate, usually caudate at the apex, often somewhat keeled, setulose-pubescent particularly on the keel.
Ovary trigonously subcylindric, very shortly pubescent, 3 (4)-locular; style 1–1·5 mm. long, glabrous.
Petals yellow, the same length as the sepals, oblanceolate, with a short ciliate claw at the base.
Androgynophore c. 0·5 mm. long, extended above into a slightly undulate annulus.
Seeds dark brown, 1–1·3 × 0·7–1 mm., oblong-ovoid.
Herbaceous or half-woody annual, 1–2 ft. high
Flowers yellow.
Stamens 30–40.