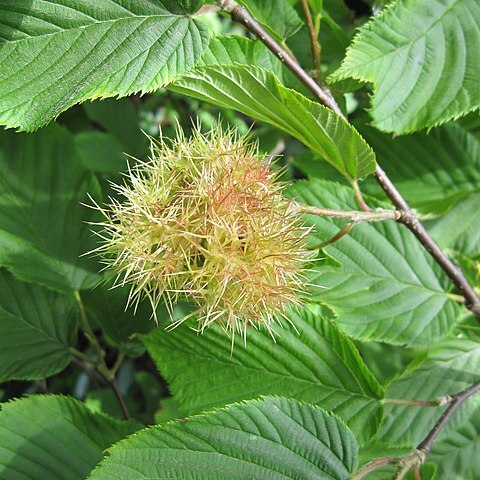
Trees to 20 m tall; trunk to 30 cm d.b.h.; bark dark gray or gray, fissured. Branchlets purplish brown, pubescent, sometimes stipitate glandular, glabrescent, with scattered, minute lenticels. Petiole 1-3.5 cm, densely pilose when young, glabrescent; leaf blade ovate-oblong, obovate-oblong, obovate, or elliptic, 5-15 × 3-9 cm, papery, abaxially bearded in axils of lateral veins, pilose and sparsely glandular, adaxially sparsely pilose especially along impressed midvein when young, base very obliquely rounded or subcordate, margin sharply and doubly mucronate serrate, apex long acuminate to caudate-acuminate; lateral veins 8-14 on each side of midvein. Male inflorescence ca. 2 cm; bracts broadly ovate, tomentulose, apex acute to acuminate; anthers purple. Female flowers 4-6 in a cluster; bracts campanulate, densely pubescent, sometimes stipitate glandular, with laciniate segments forming branching, pungent spines. Nut ovoid-globose, subcompressed, 1-1.5 cm in diam., apex pubescent. Fl. May-Jul, fr. Jul-Sep. 2n = 22.
More
A tree. It grows to about 10-20 m high. The bark is dark grey and cracked. The young shoots have silky hairs. The leaves are 4.5-16 cm long by 2.5-7.5 cm wide. They are oval and taper to the tip. They have fine teeth around the edges. They are hairy especially underneath. The flowers are yellow. The fruit is a nut. They are oval. They occur in dense clusters. They are tightly packed together. They are slightly flattened.