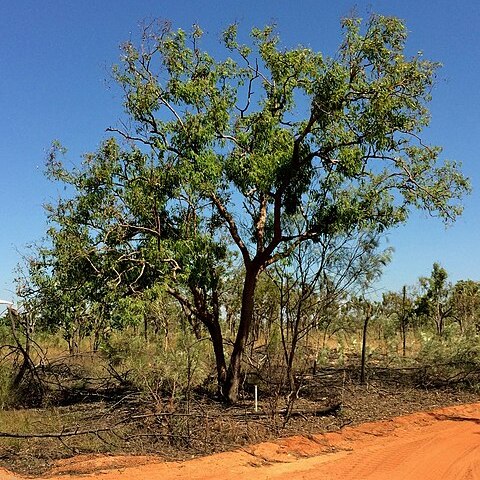
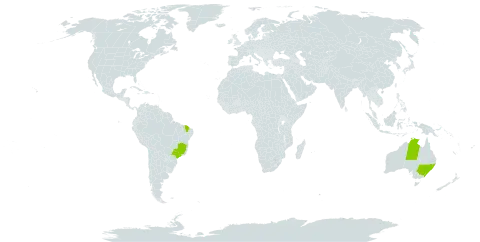
Tree to 20 m tall. Forming a lignotuber.Bark rough to the small branches, tessellated, grey and grey-brown over red-brown.Branchlets lack oil glands in the pith.Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stems rounded to square in cross-section, smooth; juvenile leaves always petiolate, opposite for ca 25 nodes, elliptic to lanceolate, to 25 cm long, 1–4 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, apex pointed, green, smooth.Adult leaves alternate, petioles 0.7–2.8 cm long; blade lanceolate to falcate, 7.8–20.8 cm long, 1–3.8 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, margin entire, apex pointed, discolorous, usually ± glossy, green, smooth, side-veins greater than 45° to midrib, reticulation very dense, intramarginal vein present and close to margin, oil glands usually visible, island, one per areole.Inflorescence terminal compound, peduncles 0.5–2.5 cm long; buds 7 or 9 per umbel, pedicels 0.2–1.2 cm long. Mature buds obovoid to narrowly pyriform, 0.9–1.4 cm long, 0.5–0.8 cm wide, scurfy (whitish scaly surface due to fragmenting rubber cuticle), scar absent (both opercula shed together at flowering), operculum shallowly rounded to conical, stamens inflexed, all fertile, anthers oblong, dorsifixed, versatile, dehiscing by longitudinal slits, style long and straight, stigma blunt and long-papillose, locules 4, the placentae each with ca 5 ± indistinct vertical ovule rows. Flowers creamy white to pale yellow.Fruit pedicellate (pedicels 0.2–1.1 cm long), elongated barrel-shaped, slightly tapering distally or, less often, slightly constricted below the orifice, 1.5–3.5 cm long, 0.8–1.6 cm wide, longer than wide (mostly 1.6–2.1 times as long as wide, rarely more), ± smooth, disc descending vertically, valves 4, enclosed.Seeds brown, 8–13 mm long, ellipsoidal with terminal wing, hilum subterminal. Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons reniform; stems rounded in cross-section, setose with short bristle-glands for up to 8 nodes then smooth; leaves always petiolate, opposite for at least 16 nodes, narrowly oblong to elliptical or lanceolate, 6.5–10(17) cm long, 0.8–3.7 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, dull or slightly glossy, green, only sparsely setose on lower leaves, smooth after ca 6–8 pairs.
More
An medium sized evergreen tree. It grows to 10-20 m high and spreads to 5 m across. The stem is erect and branching. The bark is flaky, rough and grey. The crown is compact. The leaves are dark green above and paler underneath and narrowly sword shaped. They are leathery and taper towards the tip. They are 10-20 cm long by 1.2-3.5 cm wide and have a leaf stalk which is 0.8-2.5 cm long. The young leaves are more rounded and with short stalks. The flower buds are pale green to grey and long. They occur in groups of 3 to 7. The flowers are creamy yellow. They occur in dense heads near the ends of branches. The fruit are long urn shaped capsules. These are woody and narrow towards the neck. They are 1.6-3 cm long by 1-1.5 cm wide. The seeds are yellow brown. They do not have wings.