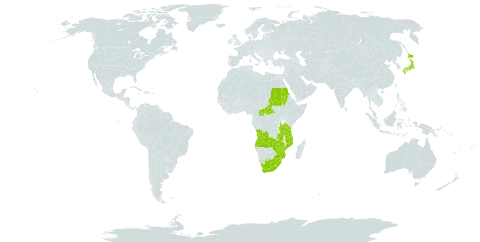
Plants usually 60-100 cm. high.. Corms 1-2 cm. diameter, producing stolons up to 18 cm. long, tunics membranous, almost papery, brown.. Foliage leaves several, plane, linear-lanceolate, shorter or longer than the stems, thin-textured.. Stem arching outward above, unbranched or (2-)3-4-branched.. Spike 4-12-flowered, strongly arched, usually flexuose, the branches diverging; bracts firm, green or becoming brown, 5-8(-15) mm. long, the outer acute, acuminate or 2-3-toothed, the inner 2-toothed.. Flowers actinomorphic, hypocrateriform, usually facing the ground, bright orange (rarely with dark markings at the tepal bases); perianth-tube cylindric-curved, 1-1.6(-2.2) cm. long, barely expanded above; tepals subequal, narrowly elliptic, obtuse, spreading horizontally, 1.2-2.8 cm. long, 3-6 mm. wide.. Filaments 1.2-3 cm. long, erect, exserted for most of their length, surrounding the style; anthers 3-7 mm. long, whitish to orange.. Style almost central, dividing opposite the anthers, branches 2-5 mm. long.. Capsules depressed globose, bright orange-red on the inside, ± 1 cm. long, 1.2-1.5 cm. diameter.. Seeds 1-2(-4) per locule, blackish, glossy, 4-5 mm. in diameter.. Fig. 10.
Perennial herb, geophyte, 0.45-1.60 m high; corm almost globose, forming stolons, tunics papery; stem erect, 7-10-ribbed. Leaves ensiform, acuminate, 200-600(-1200) x 10-30 mm; midvein prominent, margins hyaline. Bracts straw-coloured to pale orange, almost triangular, outer acuminate, 2-or 3-toothed, inner bidentate with acuminate teeth. Inflorescence a raceme of spikes, arching slightly towards ground, with ascending-spreading branches; flowers golden-orange, actinomorphic, salver-shaped; tube cylindrical, curved or nodding; lobes elliptical, spreading horizontally. Stamens exserted, symmetrically arranged, directed downwards, clasping style below; filaments white; anthers light orange; pollen orange or yellow. Style yellow, exserted, directed towards ground. Flowering time Dec.-Mar. Capsule depressed-globose, 3-lobed.
Flowers bright-orange (rarely with dark markings at the tepal bases), actinomorphic, hypocrateriform, usually directed toward the ground; perianth tube cylindric-curved, 10–16(22) mm long, barely expanded above; tepals subequal, 12–28 × 3–6 mm, narrowly elliptic, obtuse, spreading horizontally.
Geophyte, up to 1 m high. Perianth tube less than twice the length of the segments. Leaves usually up to 20 mm wide, linear-lanceolate with numerous closely spaced veins. Perianth salver-shaped. Stamens and style widely exserted. Peduncle ribbed. Flowers bright golden-orange or reddish orange.
A herb. It keeps growing from year to year. It grows 60-100 cm tall. It has oval tubers or corms. It has creeping stems. The leaves are in 2 ranks. They clasp one another at the base. They are 2-3 cm wide. The leaf blades are ribbed. The flowers are trumpet shaped. They are orange or yellow.
Spike 4–12-flowered, strongly arched, usually flexuous: bracts firm, green or becoming brown, 5–8(15) mm long, the outer acute to acuminate or 2–3-toothed, the inner 2-toothed.
Stamens symmetrically disposed; filaments 12–30 mm long, erect, exserted for most of their length, surrounding the style; anthers whitish to orange, 3–7 mm long.
Cormous geophyte, 40-130 cm. Leaves linear-lanceolate. Flowers actinomorphic, nodding, orange, filaments elongate.
Corms 10–20 mm in diameter, producing stolons up to 18 cm long; tunics membranous, almost papery, brown.
Foliage leaves several, shorter or longer than the stems, linear-lanceolate, plane, thin-textured.
Capsules c. 10 mm long, 12–15 mm in diameter, depressed globose, bright orange-red on the inside.
Seeds 1–2(4) per locule, blackish, glossy, 4–6 mm in diameter, globose, later becoming wrinkled.
Stem arching outward above, unbranched or (2)3–4-branched with the branches diverging.
Style almost central, dividing opposite the anthers, branches 2–5 mm long.
Plants usually 60–100 cm high.