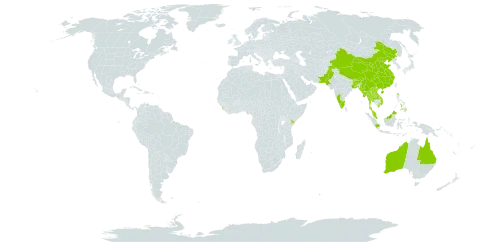
Woody scrambler or liane. Indumentum uncoloured. Branchlets with dense stellate trichomes, glabrescent. Stipules linear-subulate, 2.6–8 mm long, entire. Leaf lamina elliptic to ovate, 12–140 mm long, 5–100 mm wide; base cuneate, cordate or lobate; margin crenate with 25–30 short teeth; tip acute, acuminate; venation palminerved with 5 veins at base and 3–6 lateral veins per side of midrib further up the lamina, tertiary reticulate veins obscure; lower surface pale silver-green, venation weakly visible, with dense stellate trichomes, glabrescent; extrafloral nectaries 2 at lamina base, circular, sessile or stipitate, visible above and below. Male flowers: pedicels 3–9 mm long; sepals lanceolate-ovate, 2–3 mm long; petals obovate, 2.5–3.5 mm long; stamens 23–36. Styles 3, bifid once. Fruit ± rounded, globose, 14–22 mm long, 14–24 mm diam., with dense sessile and stalked stellate trichomes. See also Du Puy & Telford (1993: 267).
A small shrub. It grows 2-3 m tall. It can be creeping. The leaves are 4-6 cm long by 4-5 cm wide. They are hairy underneath. The base is wedge shaped and there are some teeth or divisions along the edge.