Leaf blades 3–21 × 2–14 cm, ovate, elliptic-ovate or ovate-lanceolate, acuminate at the apex, glandular crenate-serrate on the margins, sometimes shallowly and/or irregularly so and sometimes with small stipitate or sessile discoid glands in the sinuses also, usually cuneate or rounded and with a pair of subsessile or stipitate discoid glands at or near the base, chartaceous, stellate-pubescent on both surfaces when young, later glabrescent, dark green, smelling of walnuts when crushed; 3–5-nerved from the base, lateral nerves in 4–6(8) pairs, sometimes slightly impressed above when dried, prominent beneath.
Male flowers: pedicels 2–6 mm long; sepals 5, 2–3 × 1.5 mm, elliptic-ovate to ovate-lanceolate, sparingly stellate-pubescent without, glabrous within, puberulous at apex, pale yellowish-green; petals 5, 2–3 × 1–1.5 mm, elliptic-lanceolate to oblong-lanceolate, glabrous without, puberulous within, ciliate, greenish-cream in colour; disk glands free, triangular, acutely acuminate; stamens 14–17, filaments 4 mm long, glabrous, anthers c. 1 mm long; receptacle densely villous.
Female flowers: pedicels 1–2 mm long, not or slightly extending in fruit, stout, densely stellate-tomentose; sepals 5(7), 3 × 0.5–1 mm, linear-lanceolate, indumented as the male sepals, whitish; petals 0–5, shorter than the sepals, otherwise resembling the male petals; disk 5-lobed, glabrous; ovary 2 mm in diameter, ovoid-subglobose, densely stellate-tomentose; styles 3, 4–5 mm long, deeply 2-partite with the segments filiform.
Small to large tree, up to 13 m high. Leaves uniform green on both surfaces, margin dentate. Male and female flowers produced together in spikes up to 150 mm. Flowers cream or pale yellow.
Fruits 9–11 × 7–10 mm when dry, larger when fresh, trilobate-subglobose to ellipsoid, subindehiscent, sparingly to evenly stellate-pubescent, bright pinkish-orange or yellow.
Racemes 6–21 cm long, terminal, male, female or androgynous; axes sparingly to densely stellate-pubescent; bracts smaller than but otherwise resembling the stipules.
Twigs sparingly to densely stellate-pubescent at first, later glabrescent and becoming dark grey-brown.
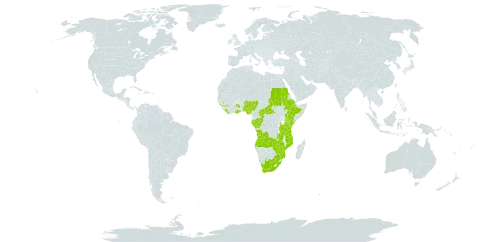
A shrub or tree up to 40 m tall, sometimes deciduous, monoecious; crown spreading.
Bark smooth or slightly roughened, soft, fibrous, light grey or greyish-brown.
Seeds 6 × 4–5 mm, compressed-ovoid, whitish, aril white.
Stipules 0.5–1 cm long, linear, soon falling.
Bole up to 12 m high, and 75 cm d.b.h.
Petioles 1.5–7 cm long, bipulvinate.
A tree. It grows 3-20 m tall.