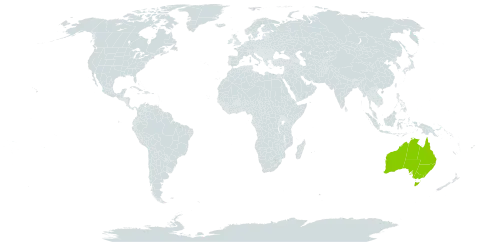
Herb, dioecious, rhizomatous, perennial, forming extensive patches to 0.5 (–3) m across and culms forming dense trailing masses; cluster and sand-binding roots present. Rhizome stout, horizontal, up to c. 20 cm long, 5–8 mm diam.; scales few, brown, scarious, partly covering a dense, yellow-to red-brown woolly pubescence. Cataphylls overlapping, red-brown, glabrous. Culms spaced to c. 1 cm apart on the rhizome, initially erect but the upper culm often flexuose, terete, striate, 25–75 cm long, 0.8–1.3 mm diam., glabrous, dull green; usually repeatedly branched; branches slender, erect or flexuose; internodes numerous, short, to c. 3 cm long. Sheaths closely appressed, scarious, striate, straw-coloured to grey, to c. 1.2 cm long, glabrous, apex acute; lamina short, erect, 1–2 mm long; with a narrow, caducous, membranous margin. Inflorescence: male and female spikelets similar, terminal on culms or culm branches or sessile in the axil of an upper node; erect, elongated, many-flowered, narrow-cylindrical, 0.5–2.5 cm long, 1.5–2.5 mm wide; spathes very small, c. 1–2 mm long, acute to obtuse, with a minute, erect mucro. Male spikelets with c. 30–60 glumes, all fertile, ovate-lanceolate, brown, acuminate to subulate, 1.7–2.2 mm long; margin thin, hyaline, membranous, occasionally ciliate; mucro to 1 mm long. Female spikelets with 1 or 2 sterile lower glumes, 10–50 fertile upper glumes. Male flowers: tepals 6, lanceolate, acute, brown with hyaline margin; 2 outer tepals keeled, 1.4–1.8 mm long, pubescent along the keel with red-brown hairs; inner tepals flat, slightly shorter than the outer tepals, glabrous; stamens 3, filaments 1.5–2.3 mm long, anthers c. 1 mm long; pistillode absent. Female flowers: tepals 6, similar to males; staminodes absent; style 2-branched, shortly connate at the base, stout, strongly recurved, almost wholly stigmatic. Capsule c. 1.5 mm long. Seed oblong, brown, 0.9 mm long, smooth with longitudinal lines of transversely-elongated rectangular cells. Culm anatomy: chlorenchyma of 1 or 2 layers of somewhat elongated peg cells, interrupted by greatly enlarged epidermal cells that meet and interrupt the parenchyma sheath over girders opposite some outer vascular bundles (mostly over alternate bundles), central cavity usually present.