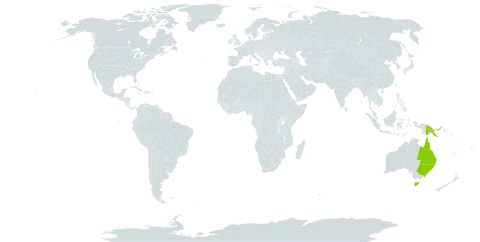
Tree to 30 m, but at high altitudes much less; bole to 50 cm diam.; buttresses to 20 cm tall and 30 cm out. Bark grey, vertically fissured; inner bark brownish, sometimes with weak white latex; sapwood cream or white; heartwood red, hard, with conspicuous medullary rays. Twigs stout, erect, cicatrose, greyish with large raised, pustular lenticels. Leafy twigs 6–11 mm diam., lenticellate, ± yellow-brown velutinous, sometimes with white latex or inhabited by ants. Apical buds with fist-shaped young leaves. Leaves 20–75 cm, imparipinnate and less often paripinnate on same tree, or apical leaflet lost, up to 6-jugate, less at high altitudes; petiole 8–20 cm, 3–5 mm diam., terete to flattened adaxially, glabrescent to pubescent or even tomentose. Leaflets opposite to subopposite, the subterminal the largest, to 28 by 10 cm, elliptic-ovate, the more proximal smaller, ovate, subglabrous or sparsely sericeous adaxially with domatia, to softly fulvous pubescent on veins adaxially and ± over whole abaxial surface, the indumentum often with longer paler hairs scattered in it, ± coriaceous, particularly at high altitudes, bases ± weakly asymmetric, acute to cuneate, apex acuminate, often abruptly so, costae c. 11–15 on each side, prominent abaxially in sicco, arcuate, linked at margin, venation brochidodrome; petiolules 0–6 mm, ± pubescent. Thyrses to c. 25 cm long, often less, axillary to supra-axillary, sometimes borne in axils of lately fallen leaves, ± erect, 1-or 2-branqhed, ± pyramidal, the axes ± fulvous pubescent, the primary branches to 6 cm long, the secondary to 5 mm or fascicles crowded distally on primary; bracts 1–3 cm, narrowly lanceolate to foliose when up to 1 cm wide and petiolate, ± fulvous pubescent; pedicels 5–8 mm; bracteoles 1–3, to 4 mm long, narrowly triangular. Flowers sweetly-scented (sweet Compositae, e.g. Helenium, Mabberley). Pseudopedicel 2–4 mm, swollen proximally near articulation, ± fulvous pubescent. Calyx 5–8 mm long and diam., cupular splitting at anthesis into (4) 5 (6) rather irregular lobes, 1–4 mm, ± densely adpressed pubescent without. Petals (4–)5(–6), 7–10 mm long, densely sericeous without, creamy white, waxy, valvate, adnate in up to proximal third to staminal tube. Staminal tube glabrous to ± pilose, especially at base within, white, with 10(–l2) rather irregular lobes, sometimes emarginate, reflexed at anthesis; anthers 10(–12), c. 2 mm long, oblong, ± included. Disk c. 5 mm long, glabrous or sometimes pilose within, margin irregularly 5-lobed to crenulate. Ovary densely pilose, (4-or) 5-locular, each locule 2-ovulate; style pilose in proximal half; stylehead short-cylindrical to subdiscoid. Capsule to 3 cm long, c. 4 cm diam., ellipsoid to depressed globose, usually rostrate, yellow-brown, cerebriform in sicco with a dense tawny tomentum, usually mixed with paler, deciduous, irritant hairs c. 2 mm long, (4–)5(–6)-locular, each locule with 1 or 2 seeds. Seeds trigonal, testa orange, with aril enveloping proximal third.
More
Tree to 30 m high; bole to 50 cm diam., with small buttresses; bark grey, vertically fissured; leafy shoots usually yellow-brown velutinous. Leaves in spirals, fist-shaped in bud, 20–75 cm long, usually imparipinnate, to 6-jugate; petiole 8–20 cm long; leaflets elliptic-ovate, to 10–28 cm long, 2.5–10 cm wide (subterminal largest), weakly asymmetric at base, acuminate at apex, subglabrous to softly fulvous hairy abaxially. Thyrses to c. 25 cm long; flowers sweetly scented; pedicels 5–8 mm long; bracteoles 1–4 mm long. Calyx tubular, c. 5–8 mm long, splitting into usually 5 irregular lobes. Petals usually 5, 7–10 mm long, creamy white, adnate to tube in lower ⅓, sericeous outside. Staminal tube glabrous to ±pilose; margin with usually 10 rather irregular lobes; anthers 10. Disc c. 5 mm long. Ovary 5-locular; locules 2-ovulate. Capsule to 3 cm long, often rostrate, yellow-brown with dense tawny tomentum usually with paler deciduous irritant hairs. Seeds up to 10, trigonal, orange.