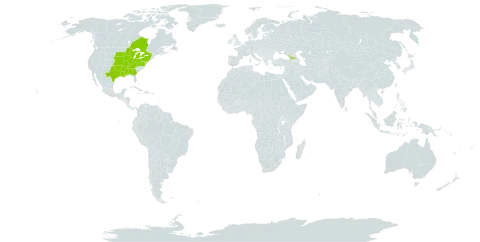
Extensively colonial; sterile corms numerous, producing a single lf and usually 1–3 stolon-like offshoots; fertile corms few, 2-lvd; lvs mottled in life, flat or nearly so; scape stout, 1–2 dm; tep 2.5–5 cm, strongly recurved-reflexed at anthesis, normally bluish-white, varying to light pink, often suffused with green or blue outside, yellow at base within, not auriculate; stigmas stout, separate, divergent from the linear-clavate style; fr ± erect, held off the ground, rounded to slightly apiculate or slightly depressed at the summit; 2n=44. Moist woods, especially on south slopes; s. Ont. to Minn., s. to Md., DC., Ga., Ky., Mo., and Okla. Mar.–May.
A bulb plant. It grows 15-30 cm high and spreads 8-15 cm wide. The leaves are long and fan outwards. The flowers are held above the leaves. They hang downwards and have petals which are pointed and curve back. The flowers are 2.5-5 cm long. They are white with some yellow. Plants go dormant after flowering.