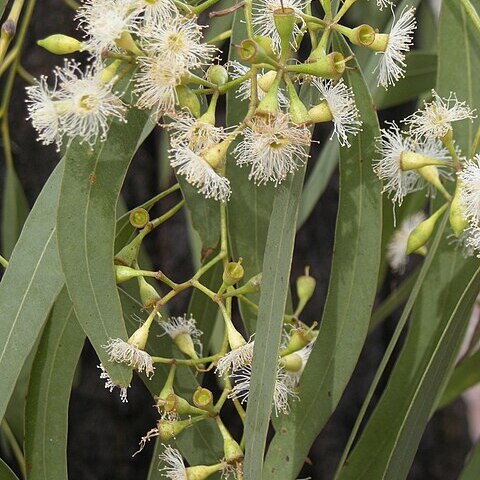
Tree to 30 m. Bark rough throughout, dark grey to black. Juvenile leaves linear to narrowly lanceolate, green or grey-green, slightly discolorous. Adult leaves narrowly lanceolate to lanceolate, acuminate; lamina 6.5–15 cm long, 1–1.7 cm wide, dull, green or grey-green; lateral veins faint, at 30°–45°; intramarginal vein up to 1 mm from margin; petiole 10–15 mm long. Conflorescence terminal, paniculate; umbels 7–11-flowered; peduncle terete to quadrangular, 4–12 mm long; pedicels 1–6 mm long, with angles sometimes continuous as ribs on hypanthium. Buds clavate or fusiform; operculum conical to hemispherical, 2–3 mm long, c. 3 mm wide; hypanthium hemispherical to obovoid, 2–3 mm long, c. 3 mm wide. Fruits hemispherical or ovoid, 4–7 mm long, 4–6 mm wide; disc narrow, level or descending; valves 3 or 4, ±level to included.
Tree to 30 m. Bark rough on trunk and larger branches or throughout, dark grey to black. Juvenile leaves elliptic to ovate, light green, concolorous. Adult leaves lanceolate to narrowly lanceolate, acuminate; lamina 10–15 cm long, 1.4–2.5 cm wide, green or grey-green; lateral veins faint, at 30°–40°; intramarginal vein up to 1 mm from margin; petiole 10–20 mm long. Conflorescence terminal and axillary, paniculate; umbels 7-flowered; peduncle terete, rarely quadrangular, 4–7 mm long; pedicels 3–6 mm long. Buds obovoid or obconical; operculum hemispherical–conical, c. 3 mm long, c. 4 mm wide; hypanthium obconical, 3–4 mm long, c. 4 mm wide. Fruits hemispherical to subcylindrical, 4–6 mm long, 5–6 mm wide; disc narrow, descending; valves usually 4, level to exserted.
Tree to 30 m with rough dark grey to black ironbark throughout.. Juvenile leaves linear to narrowly lanceolate, adult lanceolate, 5–15 cm long, 1–1.7 cm wide; petiole 1–1.5 cm long.. Umbels 7–11-flowered, arranged in panicles; peduncle terete to quadrangular, 0.4–1.2[1.5] cm long; pedicels 1–6[10] mm long with angles sometimes continuing as ribs on calyx-tube.. Buds clavate or fusiform; operculum hemispherical to conical, 2–3 mm long, ± 3 mm wide.. Calyx-tube hemispherical to ovoid, 2–3 mm long, ± 3 mm wide.. Fruits hemispherical or ovoid, [3]4–7 mm long, [3]4–6 mm wide with narrow level or descending disc and 3–4 ± flush to included valves.