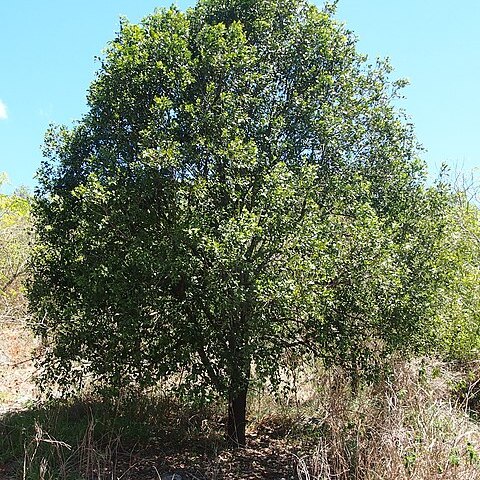
Shrub or small tree to 10 m high. Bark becoming furrowed, dark. Young shoots sparsely pubescent. Branchlets terete. Leaves: lamina broadly ovate, elliptic or obovate, to 14 cm long, very obtuse, palmiveined; petiole 5–20 mm long. Spikes often clustered or branched, up to 5 cm long, green. Tepals 5, ovate-triangular, 0.5–1 mm long, pubescent outside, green. Fruiting receptacle obovoid, 4–8 mm long, red; drupe ellipsoidal, 6–9 mm long, scurfy; tepals persistent.