Tree to 30 m high; trunk to 2 m diam.; crown rounded, branches spreading and frequently drooping to the ground in mature trees, young plants often irregularly branched and spindle-like. Bark dark brown to greenish-grey or ashen, rough; young branch-lets greenish-white or ashen, subglabrous to pubescent. Stipules spinescent, in pairs, up to 3.2 cm long, straight or slightly curved, greenish-white to light grey-brown, tips often reddish-brown when young; no prickles below the stipules. Leaves: petiole 0.5-3.7 cm long, adaxial gland absent; rhachis (1.3) 3-6(7.5) cm long, subglabrous or puberulous, with a single conspicuous gland at the junction of each of the 2(3)-10 pairs of pinnae; rhachillae (1.5)2.5-5.5(8.9) cm long; leaflets grey-green, 6-23 pairs per pinna, (2.5)4.5-9(13) x 0.75-3(5) mm, linear or linear-oblong to slightly obovate-oblong, apex rounded to subacute or mucronate, margin with or without white ciliolate hairs, glabrous or sparingly to densely appressed-pubescent ab-and/or adaxially. Inflorescences spicate, usually produced singly in the axil of a leaf, collectively forming a terminal panicle or raceme. Flowers yellowish-white to pale cream, sessile or to 0.5(2) mm pedicellate; spikes 3.5-15.7 cm long; peduncles (0.8)2-4(6.3) cm long, subglabrous to pubescent. Calyx campanulate, glabrous to pubescent, tube 0.5-1.8 mm long, lobes 0.3-0.7 mm long. Corolla often a delicate pink inside basally, tube 0.8-2.5 mm long, lobes divided almost to the base, up to 3 mm long, glabrous to pubescent. Stamen-filaments 4-6 mm long, shortly connate basally for ±1 mm; anthers 0.2-0.4 mm across, eglandular even in bud. Ovary 0.7-1.4 mm long, shortly stipitate, pilose; style glabrous or subglabrous. Pods bright orange to reddish-brown, falcate or curled into a circular coil or variously twisted, indehiscent, thick, 6-35 x (1.4)2-3.5(4.5) cm, glabrous or very rarely puberulous. Seeds light to dark brown, 9-12 x 4-8 mm, elliptic-lenticular; areole 6-9 x 4-6 mm, elliptic-lenticular.
More
A very large spreading tree. It grows up to 20-31 m tall. The trunk can be 1 m across. The trunk is light grey. The leaves are fine and drooping. The leaves can be light green or blue-green. The twigs are white and smooth. It has thorns which are straight and 4 cm long. They are white at the base and brown at the tips. They occur in pairs. Each leaf has 4-8 side branches although there can be 2-12 branches. These carry 6-23 pairs of small oblong leaflets. The leaf stalk does not have glands. It is leafless during the rainy season and has leaves during the dry season. The flowers are long cream spikes. The pods are large-about 10 cm long by 2.5 cm wide. They are red brown and twisted or almost curled into a ring. The pods do not burst open. The pods contain several hard shiny seeds. These are edible after processing. The seeds are 9-11 mm long by 6-8 mm wide.
This is a large species, reaching 30 m in height, with spreading branches and a rounded crown. Bark: rough and dark brown or smooth and greenish grey; the young branches white to ashy, zigzagging characteristically between the nodes; stipules spinescent, the spines straight, quite short, only about 2 cm long, cream-coloured with brown tips. Leaves: bipinnate, clustered at the nodes, with 3-10 pairs of pinnae, each bearing 6-23 pairs of leaflets; leaflets quite large, 3.5-9 x 1-3 mm, grey-green; rachis 3-7.5 cm long with a gland between the pairs of pinnae; petiole 0.5-3.5 cm long, without a gland. Flowers: in slender, creamy white spikes, 4-14 cm long (May-Sept.). Fruit: an unusual pod, bright orange to reddish brown, thick, indehiscent, characteristically and conspicuously curled and twisted, large, up to 25 x 5 cm.
Tree, up to 30 m high. Stipules spinescent, straight or only slightly curved. Flowers in spikes. Pods orange or chestnut to reddish brown, falcate or curled into circular coil or variously twisted. Flowers yellowish white to cream.
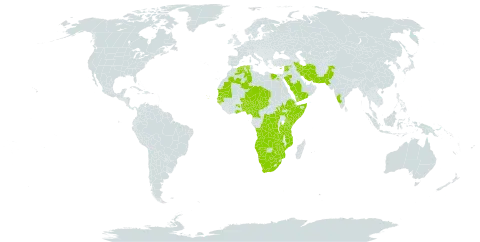
A tropical plant. It mostly grows on river banks and river flats and can grow on sandy soils. It can be damaged by frost. It grows in dry savannah but prefers damp sites and river banks. In southern Africa it grows between 40-1,070 m altitude. It grows in areas with an annual rainfall between 20-1,800 mm. It can grow in arid places.
More
Banks of seasonal and perennial rivers and streams on sandy alluvial soils or on flat land where Vertisols predominate.
The seeds are boiled, then re-boiled and the skins removed then eaten in times of food scarcity. This is done to remove toxic components. The pods are sometimes eaten. The pods are used for flavouring. Caution: The seeds can contain hydrogen cyanide and would need to be cooked.