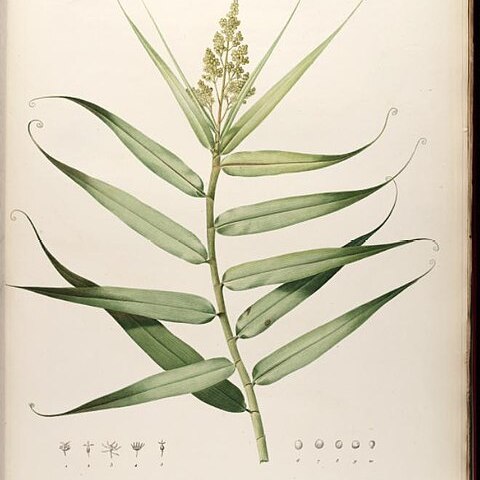
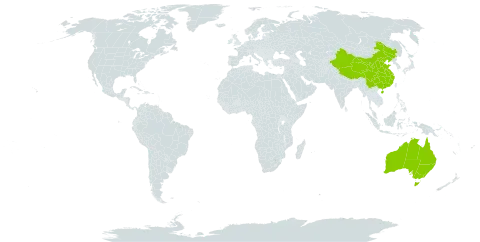
Lianas high climbing, robust, glabrous. Rhizome sympodial, diffuse. Stems terete, solid, hard, apically usually equally branched; axillary buds absent. Leaves distichous, circinate; leaf sheath tubular, closed, connected with leaf blade by a short pseudopetiole; leaf blade grasslike, stomata paracytic, apex extended into tendril; tendril simple, involutely coiled, abaxially flattened, hard. Inflorescences terminal, paniculate. Flowers bisexual or rarely unisexual, sessile, actinomorphic, 3-merous, small; perianth segments 6, in 2 whorls, free, whitish, petaloid, membranous, persistent, 3 inner ones largest. Stamens 6, in 2 whorls, exserted; filaments filiform; anthers basifixed, linear-oblong to linear, sagittate, 2-loculed, latrorse, dehiscing by longitudinal slits; pollen grains ulcerate and similar to those of grasses. Ovary superior, obtusely 3-angled, 3-loculed; ovule 1 per locule; placentation axile. Style very short; stigmas 3, linear-clavate. Fruit drupaceous with 1(or 2) seeds. Seeds globose or ± flattened; endosperm copious, starchy; embryo minute.
Shrubs or lianes. Leaves alternate, with split or entire often auricled sheathing bases; blade flat or plicate, with a long acuminate straight or cirriform tip; venation fine, parallel. Inflorescence a panicle. Flowers bracteate, hermaphrodite or dioecious, regular. Perianth subpetaloid or glumaceous, of 6 segments in 2 whorls. Stamens 6, opposite the perianth-segments; anthers basifixed, dithecous. Ovary superior, globose, 3-locular, with a short style and 3 linear stigmas. Fruit a small drupe, 3–1-seeded. Seed hemispheric or spherical
Perianth persistent, segments 6, 2-seriately imbricate, dry or somewhat petaloid
Ovules solitary in each loculus, spreading or pendulous from the central axis
Leaves sometimes ending in a tendril; leaf-sheath embracing the stem, closed
Stamens 6; anthers 2-locular, introrse, opening lengthwise by slits
Flowers hermaphrodite or dioecious, in terminal panicles
Ovary superior, 3-locular; style 3-lobed
Fruit indehiscent, fleshy or drupaceous
Seeds with copious endosperm
Erect or climbing