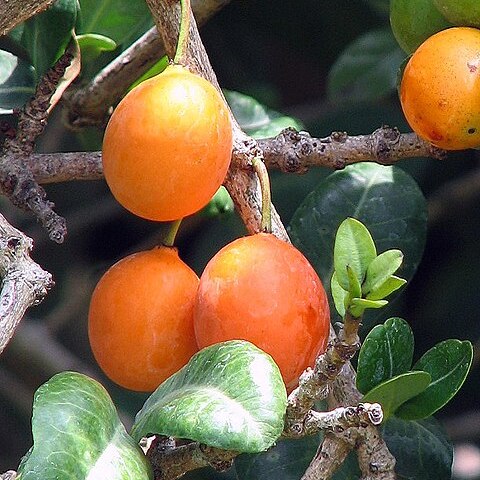
Shrub or tree up to 12 m high, narrowly triangular when young, becoming bushy and virgate; branchlets 3-whorled, thick, flattened or angled towards apex; bark moderately smooth, grey with shallow furrows producing a chequered effect; sap yellow, thick. Leaves 3-whorled, rarely 4-or opposite; blade elliptic, ovate or obovate to broadly so, 6-11 cm long, 3-5.5 cm wide, apex acute to rounded, mucronate, base broadly cuneate, rounded or cordate, midrib projecting more on lower side, lateral veins 10-12(-20), terminating in margin, tertiary venation variously conspicuous, margin entire or crenate, thickened, coriaceous, young leaves bright red; petiole 4-8 mm long, channelled above, transversely rugose. Flowers polygamous, in fascicles of 5-15 or more, in axils of older leaves on old wood; pedicels 0.8-1.3 cm long, varying in thickness. Sepals 4, unequal, in 2 opposite and decussate pairs, broadly elliptic to orbicular or triangular to transversely ovate, 1-3.5 mm long, 2-3 mm wide, concave. Petals 3-7(9), ovate, obovate or orbicular, 4.5-5 mm long, 3-4 mm wide, concave, greenish white to cream or pale yellow with orange or reddish longitudinal glandular lines. Male flowers with numerous free stamens inserted on a fleshy cushion formed by the united fasciclodes. Bisexual (and female?) flowers with fewer stamens inserted in a fleshy fasciclodal ring below the ovary; ovary ovoid to globose, 2(3)-locular, 1.5 mm long, 2 mm wide, surmounted by fleshy bilobed stigma. Berry subglobose, 1-4 cm diam., yellowish red or orange, 1-2(3)-seeded. Seeds plano-ovoid, 1-2 cm long.
Shrub or tree to 18 m high, monoecious; exudate yellow or reddish. Twigs terete, arching. Leaves opposite or 3–4-whorled, glabrous; petiole 2–7 mm long, channelled; lamina discolorous, coriaceous, oblong, elliptic or oblancelote, 3.5–11 cm long, 2–5.5 cm wide, base cuneate, rounded or cordate, apex acute, rounded, emarginate or apiculate; venation brochidodromous, primary vein raised in a groove adaxially and distinctly raised abaxially, secondary veins 9–15 pairs, pale yellow, raised on both surfaces, angle of divergence from primary vein 60–70o, intramarginal vein merges with margin. Inflorescences axillary or ramiflorous, a fascicle, 2–7-flowered. Male flowers 8–10 mm diam.; sepals 4, 2-whorled, outer pair D-shaped, c. 1 mm long, inner pair orbicular, c. 2 mm long; petals 5, orbicular, 4.5–5.5 mm long; stamens c. 30 radiating like needles in a pin cushion from globose yellow disk androecium, not adnate to petals. Female flowers c. 7 mm diam.; sepals 4, outer pair D-shaped, c. 1.2 mm long, inner pair ovate, c. 2.5 mm long; petals 5, orbicular or obovate, c. 8 mm long; disk with c. 26 free staminodes; ovary 2-locular. Fruit (not seed in Australian material) a fleshy berry, globular or obovoid, 10–30 mm long, 10–30 mm wide, orange or reddish orange, staminodes usually persistent at base of pedicel.
Leaves in whorls of 3 (rarely of 4 or opposite), coriaceous, petiolate; lamina 4–14 × 1·5–11 cm., very variable, lanceolate or oblanceolate to oblong or obovate (or rarely ± orbicular), emarginate or rounded to acute or apiculate at the apex, cuneate to rounded at the base, sometimes with shallowly crenate margin, dark to pale green above, pale green and ± glaucous below, with prominent reticulate venation on both sides, the main laterals variable in number, not always distinct from the secondary laterals, and with no visible secretory system; petiole 4–8 mm. long, channelled above, transversely wrinkled; ligule prominent.
A slow growing evergreen shrub. It can grow to 5-10 m high and spread to 5 m wide. It has a twisted trunk. Most branches come out at right angles to the stem. The leaves are tough and leathery. They are 10-15 cm long and with white veins. They are glossy and dark green. The leaves come out in whorls of three. Fruit are about 5 cm across. They have a thin skin, are bright orange and usually have 2 seeds inside. There is a layer of orange pulp around these large seeds. The flesh is edible. The fruit grow on mature wood.
Petals 3–7 (9) mm. long, 1–11/2 times as long as the inner sepals, usually 5, but sometimes up to 8 (when they are linked with the sepals by transitional forms), obovate to orbicular, greenish-white to cream or pale yellow, with ± translucent, orange or reddish longitudinal glandular lines.
Shrub or tree, up to 12 m high. Leaves 3-whorled; petioles 4-8 mm long. Flowers in fascicles in axils of older leaves on old wood; staminal or staminodial fascicles absent. Flowers greenish white to cream or pale yellow with orange or reddish longitudinal glandular lines.
Glabrous shrub or tree, (3)4·5–12(18) m. high, ± pyramidal when young, later bushy; branches striate when young, later smooth, cylindric or somewhat triangular, spreading at first, becoming virgate.
Bisexual (and female?) flowers with fewer stamens (or staminodes?) inserted in a fleshy fasciclodal ring below the ovary; ovary globose, 2 (3)-locular, surmounted by a bilobed fleshy stigma.
Flowers polygamous, in fascicles of 5–15 or more in the axils of the older leaves and on the old wood; pedicels 4–20 (35) mm. long, varying in thickness.
Male flowers with numerous apparently free stamens inserted in a fleshy cushion formed by the united fasciclodes.
Berry 1–2·5 (3) cm. in diam., obovoid to globose, orange-yellow to reddish, 1–2 (3)-seeded.
Sepals unequal, 4 in 2 opposite and decussate pairs, or 3, oblong to orbicular, cucullate.
Seeds cylindric or ± plano-ovoid, 1·5–2 cm. long.
Shrub or branching tree to 50 ft. high
Fruits yellow or red
Petals white
Dark foliage