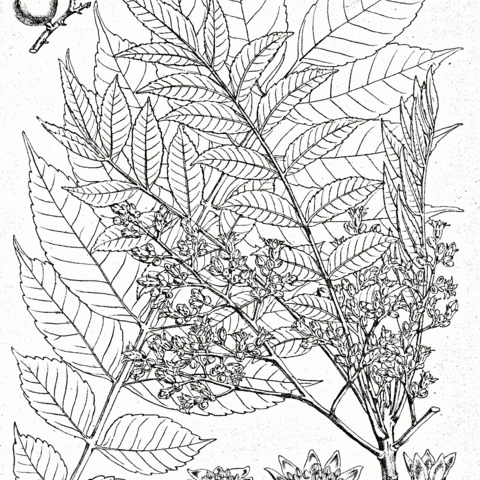
Trees 4-10 m tall; bark gray-brown, rough. Branchlets glabrous except very young parts, with conspicuous lenticels and leaf scars. Leaves with 9-23 leaflets; rachis and leaflets pubescent with long hairs, especially when young and on veins; petiolules absent to 4 mm, terminal petiolule 5-10 mm; lowest leaflet blades stipulelike, spoon-shaped or linear, 5-10 mm, early deciduous, middle blades elliptic, oblong, or lanceolate, 5-11 × 2-3 cm, base rounded, sometimes obliquely cuneate, margin sparsely serrate, apex usually narrowly acuminate; lateral veins 10-15 pairs. Panicles lateral or axillary, 7.5-19(-22) cm, densely pubescent with long hairs when young; peduncle 2-6 cm. Flowers white, yellowish white, or greenish yellow, 7-10 mm; pedicel 1-3 mm, long pubescent. Sepals deltoid, 2.5-3.5(-4) mm, pubescent on both surfaces. Petals oblong, 5-5.5 × 1.5-2 mm, pubescent with short somewhat curved hairs. Stamens slightly unequal; filaments with long hairs at base; disk lobes trapeziform or deltoid. Ovary oblong, with short stipe, sparsely pilose, especially when young; style pilose; stigma shallowly 5-lobed. Fruit globose, yellow when ripe, 11-15(-18) × (9-)11-18 mm, sometimes pubescent. Fl. Mar-Apr, fr. Apr-Oct.
More
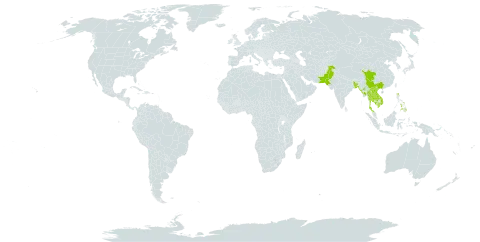
A tree which loses its leaves during the year. It grows 20-35 m tall. The trunk can be 60-180 cm across. It can have small buttresses. The leaves have leaflets along the stalk. There are 5-9 pairs of leaflets and an odd one. They are 5-15 cm long by 3-6.5 cm wide. They are oval to sword shaped. There are shallow round teeth along the edge. They are slightly hairy. The flowers are yellow in large loose flower clusters at the ends of branches. The fruit is fleshy with a hard covering around the seed. It is round and black. It is sour and edible.