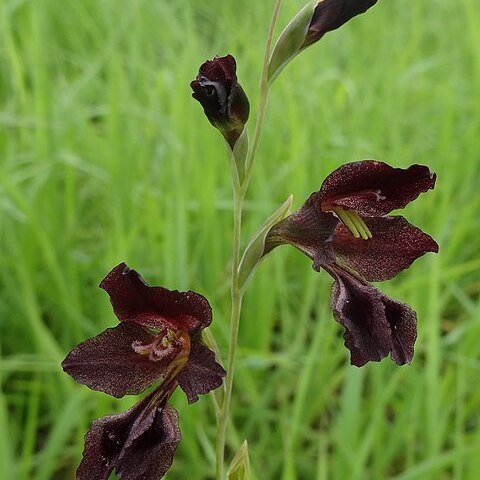
Flowers cream-coloured to light-purple with the upper tepals flushed light-to deep-purple, the lower lateral tepals each with a deep-purple spade-shaped mark in the distal third surrounded by a lighter area or partly to entirely dark-purple, sometimes with pale markings on the lower tepals; perianth tube 10–12 mm long, curving outward between the bracts, widening near the mouth; tepals unequal, the uppermost 15–20 × 9–12 mm, larger than the others and arching over the stamens, the upper lateral tepals smaller directed forwards and curving outwards distally, the 3 lower tepals (10)12–15 × 6–9 mm and horizontal to down-curved, joined with the upper laterals for c. 5 mm and usually exceeding the uppermost when viewed in profile, narrowed below into claws, the limbs abruptly expanded.
A slender herb. It grows 30 cm high. It grows from a corm. The corm has thickened fibres around it. The corms are 2-3 cm across. The leaves develop separately after flowering. There are 3-4 leaves on the flowering stem. They form a sheath around the stem or have blades 5 cm long. There are single leaves on no flowering plants and these are 15-20 cm long. There are 5-10 flowers on a flowering stalk. The flowers are dull purple. The fruit is a capsule 12-18 mm long
Foliage leaves of the flowering stem 3–4(5), entirely sheathing or with blades to 5(10) cm long, imbricate, narrowly lanceolate to linear, the margins and midribs hyaline and usually slightly thickened (hysteranthous foliage leaves on separate shoots are not produced); leaves of non-flowering plants solitary, 15–20 cm long, 4–6(12) mm wide, linear, usually with slightly thickened margins.
Spike (3)5–10(15)-flowered, slightly flexuous, inclined; bracts green, 10–15(20) mm long, attenuate, rather soft-textured, the margins often membranous, the inner bracts somewhat shorter to nearly as long as the outer.
Style dividing opposite the upper half of the anthers, style branches 2–2.5 mm long, usually reaching nearly to the apices of the anthers, rarely exceeding them.
Corms (10)15–20(30) mm in diameter; tunics fibrous, pale straw-coloured, fibres mostly vertical and often thickened and claw-like below.
Stem erect, unbranched (rarely branched), usually slightly flexed above the sheath of the upper leaf.
Filaments 6–8 mm long, exserted c. 4 mm; anthers 5–8 mm long.
Capsules (10)12–18 mm long, ovoid to ellipsoid.
Plants 30–60 cm high.