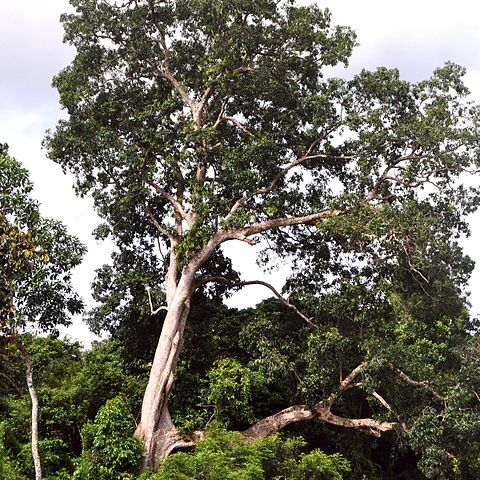
Large tree up to 50 m high and 115 cm ø, sometimes buttressed when old. Bark light fawn brown, or greyish when old, dippled scaly with small flakes. Leaves coriaceous, elliptic-oblong or narrowly elliptic, or oblanceolate, 12-28(-36) by 4-7½(-9) cm, glabrous; base cuneate, sometimes subcordate; apex obtuse; nerves 17-30 pairs, elevated on both surfaces; veins reticulate, distinct on both surfaces; petiole 0-3 cm. Panicles 6-25 cm long, glabrous, sometimes sparsely puberulous and glabrescent; pedicels articulated, 3-6 mm. Flower-buds ellipsoid, 3-4 by 1½-1¾ mm, obtuse. Calyx 3-4 mm long, bursting irregularly, glabrous, sometimes sparsely puberulous at the apex. Petals white, contorted, elliptic-lanceolate, oblanceolate, or linear, 7½-13 by 2-3 mm, glabrous outside, papillose inside; the central part of the basal 2-3 mm longitudinally adnate to the torus. Stamens 5, 4-5½ mm; filaments glabrous; anthers oblong, ⅔-l mm long. Torus cylindric, 2-3 mm long. Ovary subglobose, 1-1½ mm ø, glabrous; stipe 0-¾ mm; style lateral, 2½-372 mm. Drupe on a centric stalk (c. ½ cm), subglobose, 3½-5 cm ø, pinkish brown, with irregular crests and protuberances; without enlarged petals; embryo subglobose, 2-3½ cm ø; cotyledons incompletely fused, free on one side, free part c. 1/5 cm deep.
More
A large tree. It grows 50 m tall. The trunk can be 1.2 m across. It can have buttresses. The sap causes irritations. The leaves are narrowly oval and have a rounded tip. They are 8-28 cm long by 4-9 cm wide. They have short leaf stalks. The flowers are white and irregular. The fruit is a flattened round shape and 5 cm across. The fruit is pinkish-brown and have irregular projecting parts.
Chiefly in coastal regions, in peat-swamps, occasionally inundated areas, gregarious along riverbanks, at low altitude, sometimes in inland forest up to 800 m (Palembang). Fl. May-Dec.; fr. Jan.-Dec.G. renghas is one of the important constituents of the rapak type of swamp forest, that is swamp forest without peat formation and sometimes temporarily seasonally with a low water level, associated with spp. of Coccoceras, Alsionia, other Gluta spp., Ficus retusa, Mangifera gedebe, Lager-stroemia, etc. It is also very common on and near levees of sluggish downstream rivers, leaning from the riverbanks in the freshwater tidal reaches. In such deep marshy places the stem-base is often conically thickened (ENDERT, l.e.).
More
A riverside tree of tidal freshwater reaches. Chiefly found in coastal regions, in peat swamps, occasionally inundated areas, gregarious along river banks, usually at low elevations, sometimes in inland forests up to 800 metres.
A tropical plant. It grows along rivers. It is mostly in coastal regions and in peat swamps. It can grow up to 800 m above sea level.
Uses. The timber is very strong, durable, reddish brown, and with splendid markings. It has been used for building material of houses and canoes and for making handsome furniture. See HEYNE Nutt. Pl. 1927 972 CORNER l.e. remarked, however, that the heart-wood is not red-brown as in the other Gluta spp., but pale pinkish.The seed can be eaten after roasting (BURKILL).
More
CAUTION: The sap is poisonous. The seeds are eaten after roasting.