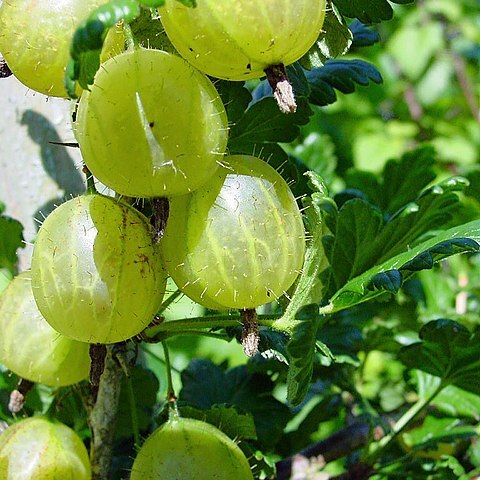
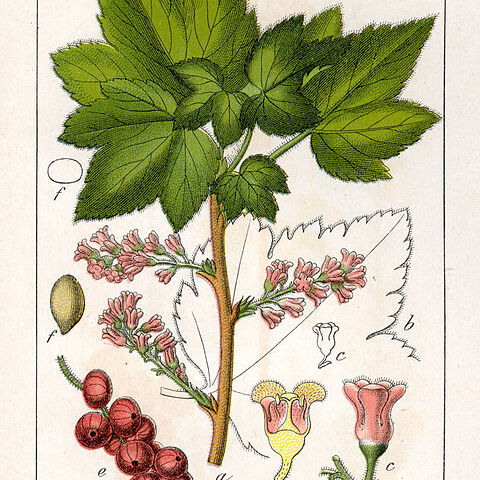
Deciduous or evergreen shrubs, sometimes dioecious; indumentum of glandular and eglandular trichomes or sessile glands; stems sometimes armed, sometimes climbing, prostrate or horizontal and subterranean. Leaves alternate to spirally arranged, simple, usually trilobulate or palmately lobed, palmate venation, petiolate; stipules present. Inflorescence racemose or in few-flowered clusters, bracteate, usually pendulous. Flowers actinomorphic, usually bisexual, 5-merous, rarely 4-merous, epigynous, hypanthium free or adnate to ovary. Sepals sometimes petaloid, persistent in fruit. Petals free, often shorter than sepals, rarely absent. Stamens opposite sepals; anthers 2-locular, dehiscent by longitudinal slits. Gynoecium 2-carpellate. Ovary inferior to semi-inferior, 1-locular; styles 2, fused near base to almost completely; stigmas 2. Fruit a berry. Seeds few to numerous, with outer mucilaginous layer and copious oily endosperm.